Cloud data center location PK Microsoft first IBM second
At present, various cloud service providers tend to use the number of data centers as a promotional capital, such as Microsoft's 12, SoftLayer's 9, and Amazon's 8. What kind of protection will multiple data centers provide, and where is the importance. Recently, David Mytton of Gigaom explained in detail the importance of geographical location selection, and listed the specific locations and number of data centers configured by some giants, as well as the reasons for selection.

Now, the competition in the cloud infrastructure market is very fierce, and every manufacturer is trying to make themselves different. The construction of infrastructure requires a lot of funds, so it is more important to choose the right location to allocate assets. Cloud providers can innovate on products or technology levels, but location is equally important. What is the reason?
Why is location important?
Diversified locations are important for the following reasons:
Redundancy: Compared with the possibility of server failure, power failure in the entire data center is not common, but it may also occur. In order to prevent power outages, software defects or extreme weather, it is important to distribute the load to multiple, independent facilities. This not only enables data redundancy across data centers, but also across regions, so local problems (such as bad weather or electrical failures) can be avoided. Data centers need to be close to each other to reduce latency and ensure geographical separation.
Data protection: Different types of data have different location requirements, such as the need to keep personal data in the EU.
User delay: In some applications, the response time to the end user is very important, so it is best to let the data center close to the user, and the ability to send traffic to different regions will help to achieve these. Although some can use CDN, connectivity is usually required.
It is not cheap to deploy data centers worldwide, which is the advantage of large cloud providers. It is not just to allocate equipment and personnel for the data center, but more important innovation comes from the efficiency of those facilities. Does this mean that using the local geographical environment or building your own power system can make the data center more environmentally friendly? These will help to reduce prices only when they reach the real scale.
Current situation
Different suppliers have the concept of region, or the data center is in a specific region. Usually, they are divided into multiple regions, so redundancy can be achieved in the region, but the real redundancy is not enough, because the whole region may fail, or may encounter storm like regional events. Therefore, true geographical separation is very important:
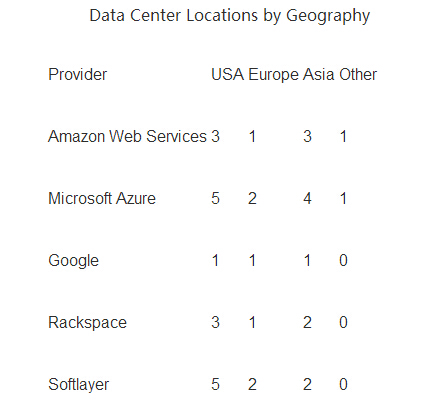
Azure leads with 12 regions, followed by 9 Softlayer, 8 Amazon, and 6 Rackspace. Google is relatively backward, with only three.
Giant site selection
For a long time, Amazon has only one data center in Europe (although it has changed with the establishment of a new center in Germany), which is strange. If you want to maintain redundancy, you need two data centers next to each other, or latency will be a problem. For example, replication of the production database between two data centers will be delayed longer if data is sent across the ocean (for example, from the United States to Ireland). It would be better to copy between Ireland and Germany!
Since 2014, Softlayer is also being promoted to other regions with the claim of spending 1.2 billion dollars in the new data center. Recently, it launched data centers in Hong Kong and London. Next, there are more plans, including two in the northern United States, two in Europe, two in Brazil, the United Arab Emirates, India, China, Japan and Australia.
The most disappointing thing is Google, which spends a lot of money on infrastructure. In fact, there are many global data centers that are not part of Google Cloud. Of course, Google is new to the cloud market. Most of its demand comes from search, Gmail and other products, and consumer demand will dominate. Given the speed with which Google has launched new features, if it really wants to compete with others, it will soon make progress.
About China
I specifically excluded China from the above data, but it is still an interesting case. The problem is that even if the domestic connection is very good (in some regions), cross-border will significantly increase delay and packet loss. Microsoft and Amazon both have data centers in China, but they need a separate account, which usually must be applied in China. Softlayer announced the establishment of a data center in Shanghai. It is worth noting whether it can connect to the global VPC and has good throughput? For Google, it left China publicly four years ago, so it is impossible to launch a data center here.
Obviously, position will be a competitive advantage. At present, Microsoft occupies the first place, but it will lose to Softlayer soon. Considering the amount of investment, it is worth noting where cloud availability will expand next.

