rpm -Uvh http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/7/x86_64/e/epel-release-7-2.noarch.rpm
rpm -Uvh http://rpms.famillecollet.com/enterprise/remi-release-6.rpm
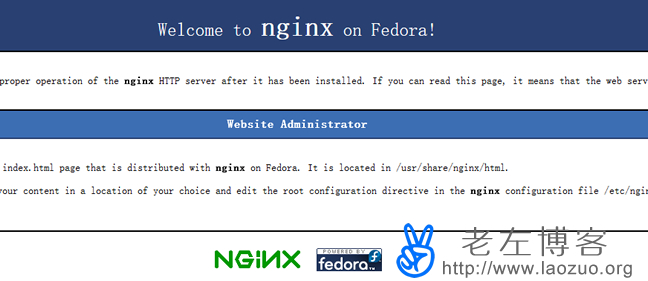
yum install nginx -y
systemctl start nginx
systemctl enable nginx
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=80/tcp --permanent$ sudo firewall-cmd --reload
yum --enablerepo=remi,remi-php56 install mariadb-server mariadb -y
systemctl start mariadb
systemctl enable mariadb
NOTE: RUNNING ALL PARTS OF THIS SCRIPT IS RECOMMENDED FOR ALL MariaDB
SERVERS IN PRODUCTION USE! PLEASE READ EACH STEP CAREFULLY!
In order to log into MariaDB to secure it, we'll need the current
password for the root user. If you've just installed MariaDB, and
you haven't set the root password yet, the password will be blank,
so you should just press enter here.
Enter current password for root (enter for none):
OK, successfully used password, moving on...
Setting the root password ensures that nobody can log into the MariaDB
root user without the proper authorisation.
Set root password? [Y/n] y
New password:
Re-enter new password:
Password updated successfully!
Reloading privilege tables..
... Success!
By default, a MariaDB installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone
to log into MariaDB without having to have a user account created for
them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation
go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a
production environment.
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] y
... Success!
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This
ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network.
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] y
... Success!
By default, MariaDB comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can
access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed
before moving into a production environment.
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] y
- Dropping test database...
... Success!
- Removing privileges on test database...
... Success!
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far
will take effect immediately.
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y
... Success!
Cleaning up...
All done! If you've completed all of the above steps, your MariaDB
installation should now be secure.
Thanks for using MariaDB!
yum --enablerepo=remi,remi-php56 install php-fpm php-common php-mysql php-opcache php-pear php-gd php-devel php-mbstring php-mcrypt php-cli php-pdo php-xml -y
service php-fpm start
chkconfig php-fpm on
user nginx;
worker_processes 1;
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
gzip on;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
vi /etc/nginx/conf.d/laozuo_org.conf
server {
listen your_public_ip_address:80;
server_name www.laozuo.org;
root /var/www/www.laozuo.org;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
charset utf-8;
location / {
}
location = /robots.txt { allow all; access_log off; log_not_found off; }
location = /favicon.ico { allow all; access_log off; log_not_found off; }
error_page 401 /401.html;
error_page 403 /403.html;
error_page 404 /404.html;
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location ~ \.php$ {
root /var/www/www.laozuo.org;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_intercept_errors on;
fastcgi_buffer_size 4K;
fastcgi_buffers 128 4k;
fastcgi_connect_timeout 50;
fastcgi_send_timeout 40;
fastcgi_read_timeout 40;
try_files $uri =404;
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+\.php)(/.+)$;
include fastcgi_params;
}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
# location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
# }
}
mkdir /var/www/www.laozuo.org
chmod 777 /var/www/www.laozuo.org
systemctl restart nginx















