Overview of steam coal
(1) Definition of coal
Coal is a kind of solid combustible mineral formed by plant remains buried underground through long and complicated biochemical, geochemical and physicochemical processes. It is not only an indispensable main fuel for industry, agriculture and people's life, but also an important raw material for metallurgy, chemical industry, medicine and other departments.
(2) Formation of coal
All kinds of coal are products of certain coalification stage. The diversity of coal forming plants and the ever-changing conditions in the long coal forming process determine the diversity, complexity and heterogeneity of coal.
Coal forming process
| Coal forming sequence |
Plant → peat → lignite → bituminous coal → anthracite |
| Transition phase |
The first stage is peatization stage |
The second stage of coalification |
| Diagenetic stage |
Metamorphic stage |
| Transition conditions |
Water, bacteria, Thousands to tens of thousands of years
|
Underground (not too deep), Millions of years
|
Underground Over tens of millions of years
|
| Main influencing factors |
Biochemical action |
Pressure (pressurized water loss), Physicochemical effect
|
Temperature, pressure, time, Mainly chemical action
|
Relationship between coal metamorphic degree and carbon content
|
peat |
lignite |
Bituminous coal |
anthracite |
| C/%( Combustible basis) |
50~60 |
60~74 |
74~90 |
90~98 |
Coal is mainly composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), sulfur (S) and some rare elements and minerals. The content of moisture, ash, volatile and fixed carbon in coal can be determined from industrial analysis.
(3) Classification of coal
According to the degree of coalification, the overall classification of various types of coal is shown in the following figure (see the appendix for specific concepts and characteristics).
Classification of coal in China
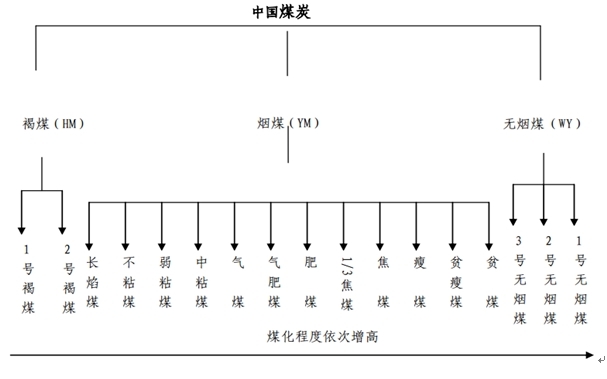
The current national standard for coal classification in China is GB5751-2009 (see Appendix I). This standard is a comprehensive technical classification standard from lignite to anthracite. Coal in nature is divided into 14 categories, among which lignite and anthracite are divided into 2 and 3 sub categories respectively.
(4) Classification and use of steam coal
one Definition and characteristics of steam coal
In a broad sense, all coal used for generating power for the purpose of power generation, locomotive propulsion, boiler combustion, etc. belongs to power coal, which is called power coal for short.
The quality of coal used in thermal power plants is an important basis for boiler design and production process control. The characteristics of fuel coal include two aspects: coal characteristics and ash characteristics. Coal characteristics refer to moisture, ash, volatile matter, fixed carbon, element content (carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur), calorific value, ignition temperature, grindability, particle size, etc. These indicators are directly related to combustion, processing (such as grinding into pulverized coal), transportation and storage. Ash characteristics refer to the chemical composition, characteristics under high temperature and specific resistance of coal ash. The cleanliness of these characteristics after combustion steel products Corrosivity and ash removal have a great impact.
two Type of steam coal
Steam coal mainly includes lignite, long flame coal, non caking coal, lean coal, gas coal and a small amount of anthracite (see the appendix for specific coal types). As for commercial coal, it mainly includes blended coal, medium coal, fine coal, and fine coal.
three Use of steam coal
Coal accounts for 26.5% of the world's primary energy consumption, which is 37.3% lower than that of oil and 23.9% higher than that of natural gas. Worldwide, steam coal production accounts for more than 80% of the total coal production. The main area of coal consumption in the United States is power generation. In 2010, the consumption reached 976 million tons, accounting for 93.1% of the U.S. coal consumption. In foreign countries, the vast majority of steam coal is used for power generation, and industrial boilers also have some consumption. More than 65% of China's steam coal consumption structure is used for thermal power generation; The second is coal for building materials, which accounts for about 20% of the consumption of steam coal, and the coal consumption for cement is the largest; The rest of steam coal consumption is distributed in metallurgical, chemical and other industries and civil use.
(5) Physical and chemical properties of coal
one Physical properties of coal
The physical properties of coal refer to the external performance of certain chemical composition and molecular structure of coal. It is determined by the original material of coal forming and its accumulation conditions, transformation process, coalification degree, weathering degree, oxidation degree and other factors. It includes color, luster, pink, specific gravity and unit weight, hardness, brittleness, fracture and conductivity.
two Chemical properties of coal
The chemical composition of coal is very complex, but it can be divided into organic matter and inorganic matter, with organic matter as the main part.
The organic matter in coal is mainly composed of five elements: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and organic sulfur. Among them, carbon, hydrogen and oxygen account for more than 95% of the organic matter. In addition, there are very small amounts of phosphorus and other elements. The element composition of organic matter in coal varies regularly with the degree of coalification. The inorganic matter in coal is mainly water and minerals, which reduce the quality and utilization value of coal, most of which are harmful ingredients in coal.
The chemical composition and content of coal can be understood through element analysis, and the properties of coal can be preliminarily understood through industrial analysis, and the types and uses of coal can be roughly judged. The industrial analysis of coal includes the determination of moisture, ash, volatile matter and calculation of fixed carbon (see appendix for details).
(6) Coal mining and processing
one . Coal mining
Coal mining has always been the hardest work. At present, greater efforts are being made to improve working conditions. According to the different burial depth of coal resources, it can be generally divided into two ways: mine mining (deeper burial) and open-pit mining (shallower burial). The proportion of opencast resources in the total resources is an important indicator to measure the advantages and disadvantages of mining conditions. In China, the reserves that can be opencast only account for 7.5%, so coal mining in China is mainly mine mining.
two . Coal processing
China's coal based primary energy pattern is difficult to change for a long time. The main problems of coal are low energy utilization efficiency and serious environmental pollution. The coal processing before coal utilization is to transform coal into electric energy, liquid fuel and gas fuel efficiently and cleanly through coal washing, power coal blending, briquette, water slurry coal and other processing technologies, so as to solve the problems of low energy utilization efficiency and serious environmental pollution.
1) Coal washing technology
Coal washing, also known as coal preparation, is to make use of the differences in physical and chemical properties of coal and impurities (gangue), effectively separate coal and impurities through physical, chemical or microbial separation methods, and process coal into coal products with uniform quality and different uses. Coal washing can improve coal quality and energy utilization efficiency, reduce emissions of pollutants from coal combustion and waste of transportation capacity.
2) Power coal blending technology
Based on disciplines and technologies such as coal chemistry, coal combustion dynamics and coal quality testing, the power coal blending technology is a low cost and easy to industrialize technology that provides coal products that can meet the requirements of different coal-fired equipment by screening, crushing, mixing in different proportions and adding additives to individual coals of different types and qualities.
3) Briquette technology
Briquette is a kind of coal product with certain shape and certain physical and chemical properties formed by mixing one or more kinds of pulverized coal with a certain proportion of binder or sulfur fixing agent under a certain pressure. Compared with raw coal, the former can significantly improve the thermal efficiency and reduce the pollution of coal combustion.
4) Coal water slurry technology
Coal water slurry (CWM) technology is a new way to use coal instead of oil, which was produced in the worldwide oil crisis in the 1970s. Its main technical feature is that coal, water and some additives are added into the mill, and after grinding, they become a kind of flowing coal based fluid fuel similar to petroleum.
(7) Quality and weight inspection of steam coal
one Quality inspection
At present, there is no special national standard for steam coal in China. The state has issued corresponding national standards for some aspects of coal products, such as classification, classification of varieties and grades, sampling, sample preparation, industrial analysis methods, calorific value and other indicators. Zhengshang Office has selected calorific value index as the pricing index for delivery and acceptance of steam coal, and has also made relevant regulations on total sulfur and water. Volatile matter, ash content, ash melting point and other indicators shall be published by the Seller according to the inspection results of the designated quality inspection agency. The details are as follows:
1) Calorific value
Calorific value , The heat generated by the combustion of unit mass of coal, in kilocalorie per kilogram (Kcal/kg). The calorific value index of steam coal is the low calorific value on the received basis.
2) Total sulfur
Total sulfur refers to the sum of inorganic sulfur and organic sulfur in coal. Dry basis, also known as dry basis, is based on coal in the assumed anhydrous state.
3) Total water
The total water of coal refers to the total water including the internal water and external water of coal.
4) Other indicators
In addition to the above indicators, volatile matter, ash melting point, ash content, etc. are also the indicators concerned by steam coal related enterprises. However, in spot trade, these indicators generally only stipulate the acceptance range and are not included in settlement.
two Weight inspection
The weight inspection of steam coal shall be conducted by the quality inspection institution or measurement institution designated by the Exchange. Unless otherwise agreed by both parties, when the Buyer uses the ship to receive the goods, the weight shall be measured through the draft gauge; When the Buyer receives goods with the vehicle, the weight shall be measured by the weighbridge. As the draft is visually measured, the uncertainty is large. When the ship receives the cargo, it is specified that the general ship weight error is within ± 500 tons.
2、 Production of steam coal in China
(1) Regional distribution of steam coal resources in China
In terms of regions, China's steam coal resources are mainly concentrated in North China and Northwest China. The thermal coal resource reserves in North China account for 46.09% of the verified thermal coal resource reserves in the country, and that in Northwest China is as high as 39.98%, that is, the thermal coal resource reserves in the "two northern" areas account for more than 80% of the country. However, the industrial developed East China only accounts for 1.77% of the national steam coal reserves, and the northeast and central south regions only account for 5.02% of the national steam coal reserves.
(2) Distribution of steam coal in China
The steam coal in China mainly includes non caking coal, long flame coal, lignite, anthracite, lean coal, weak caking coal, natural coke and some unclassified coal. In China's steam coal reserves, non caking coal is the largest, accounting for 21.83% of the verified steam coal reserves; The second is long flame coal, accounting for 20.07% of the verified resource reserves of steam coal; The third is lignite, accounting for 17.69% of the verified resource reserves of steam coal; The fourth is anthracite, accounting for 15.24% of the verified resource reserves of steam coal; Weak caking coal is the least reserves, accounting for only 2.18% of the verified resource reserves of steam coal.
Among steam coal, non caking coal has the lowest ash content, with an average of 13.48%, and lean coal has the highest ash content, with an average of 19.51%. The average ash content of steam coal resources in China is 17.06%, belonging to medium ash content. Among steam coal resources, lignite has the lowest sulfur content (0.55% on average), and lean coal has the highest sulfur content (1.67% on average). The national average sulfur content of steam coal is 0.86%, which is lower than the average sulfur content of coking coal (1.06%) and belongs to medium sulfur content. The average gross calorific value (Qgr, ad) of steam coal on air drying basis is 25.52 MJ/kg, and the lowest is lignite, which is less than 20 MJ/kg on average.

