I Early indica rice summary
(1) The classification of early indica rice, commonly known as rice, is a staple grain variety in China, which can be divided into indica rice and japonica rice. The grain of indica rice is generally long oval and slender, while that of japonica rice is generally oval. According to different sowing date, growth period and maturity period, rice can be divided into early rice, middle rice and late rice. Early rice is almost a single indica rice, namely early indica rice. Early indica rice is the earliest rice crop on the market, and also the first grain crop planted and harvested in the same year.
Early indica rice can be divided into ordinary early indica rice (conventional) and high-quality early indica rice. Ordinary early indica rice is generally used for storage, while individual processing enterprises mainly process high-quality early indica rice. The proportion of high-quality early indica rice as hybrid rice is also large. Ordinary early indica rice and high-quality early indica rice are mainly distinguished according to grain type and belly white. According to the survey, the high quality rate of early indica rice, medium indica rice and late indica rice is estimated to be 15%, 28% and 76%.
In spot, early indica rice can also be divided into long grain type and short grain type. Their uses are different and their prices are different. The short grain type is mainly used for rice flour, and the long grain type is mainly used for rations. The spot market will purchase and store the two separately. Generally, long grain yield: short grain yield=6:4. (2) Characteristics of early indica rice Early indica rice is an indica rice with a shorter growth period and an earlier harvest period. Generally, the rice grain is white in the belly and less horny. The quality of early indica rice is worse than that of mid late indica rice. Early indica rice is loose in quality, poor in pressure resistance, easy to produce broken rice during processing, low in yield and poor in eating quality. However, medium late indica rice is solid, with good pressure resistance, less broken rice during processing, and higher rice yield. However, early indica rice also has many quality advantages that can not be replaced by mid late indica rice.
1. Early indica rice has abundant rainfall, sufficient light and heat, few pests and diseases, and less disastrous weather during its growing period, which makes it easier to obtain stable and high yield. In addition, various regions actively develop fine varieties and promote new technologies, the area of improved varieties has expanded, and the unit yield of early indica rice has steadily increased.
2. Early indica rice has low water content and storage tolerance.
3. Early indica rice has a wide range of uses. It can be used as food, feed, brewing, food and other industrial raw materials.
4. The early indica rice consumption market is large. Farmers, some low-income urban residents and migrant workers mainly eat early indica rice. The demand for feed grain and industrial grain for early indica rice is also large.
5. Early indica rice has good nutritional quality. The protein content and quality of early indica rice were significantly better than those of mid late rice.
6. Early indica rice has high hygienic quality. As the amount of chemical fertilizer and pesticide applied to early indica rice is relatively small, and the health quality of early indica rice is relatively high, with the improvement of the quality of early indica rice and the development of variety diversification, there are still a considerable number of consumer groups at present and in the future.
7. Early indica rice varieties have good quality consistency and are easy to be standardized. There are fewer high-quality varieties of early indica rice, and the difference between varieties is relatively small. Early indica rice is easier to standardize. There are many high-quality varieties of mid late indica rice. The internal quality and price of different varieties vary greatly, and the yield of high-quality varieties accounts for a large proportion. Therefore, standardization is relatively difficult. (3) Generally, the growth stage of early indica rice can be divided into three stages during the natural growth and development of rice. It is a simple vegetative growth period from seed germination to the beginning of young spike differentiation, forming roots, stems, leaves and other vegetative organs; The period from the beginning of young panicle differentiation to the beginning of heading is the period of vegetative growth and reproductive growth, and the last three leaves and panicles are formed; Heading to maturity is a simple reproductive growth period, which goes through flowering, milk ripening, waxy ripening, and ripening. It is customary to divide the growth and development process of rice into "two stages and four stages", that is, the boundary is the beginning of differentiation of young panicles. Before the beginning of differentiation of young panicles, it is called the vegetative growth stage, and after the beginning of differentiation of young panicles, it is called the reproductive growth stage. In order to master the growth process in high-yield cultivation, it is divided into seedling stage, tillering stage, young ear formation stage and flowering, filling and fruiting stage. In actual operation, the seedling stage of transplanting and transplanting is the seedling stage. After transplanting, it is called the Honda stage. It is also divided into three stages, namely, the early stage, from returning to green after transplanting to high tillering; In the middle stage, rice panicle differentiated and formed; In the later stage, from the beginning of panicle to flowering to filling and maturity.
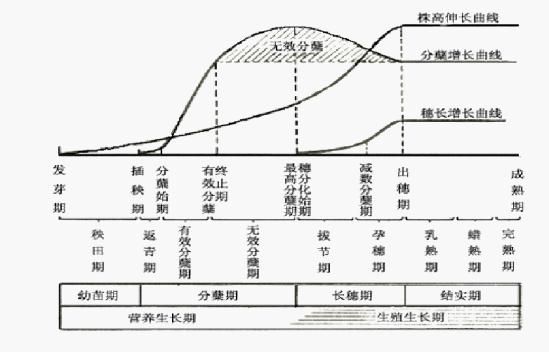 Growth stages and periods of early indica rice
Growth stages and periods of early indica rice In different regions and different cultivation seasons, the length of the growth period of rice varieties basically depends on the comprehensive effect of the "three properties" of the varieties. The three properties are light sensitivity, temperature sensitivity and basic nutritional growth. The three properties of rice varieties are the essence of determining the length and change of the growth period of varieties. The majority of early rice varieties have weak photosensitivity, medium temperature sensitivity, short to medium basic vegetative growth period, and no varieties with strong photosensitivity and long basic vegetative growth period; Middle season rice varieties, most of which have a long basic vegetative growth period, moderate to strong temperature sensitivity and weak light sensitivity; Late rice varieties have strong photosensitivity, short to medium basic vegetative growth period, and strong to medium temperature sensitivity. Generally, early rice is 90-125 days in the whole growth period (sowing maturity), middle rice is 125-150 days, and late rice is more than 150 days.
The early indica rice in China generally enters the large-scale harvesting stage in the middle and late July every year, and the early indica rice comes into the market in August; In the middle of September, the harvest of middle season rice and one season of late rice began, and in October, middle season rice and one season of late rice came into the market successively; In November, the harvest of new late indica rice and late japonica rice was completed, and the main production area of double cropping rice ushered in the late rice season.
Rice growing period of early indica rice in major provinces in 2007
| month |
Jiangxi |
Hunan |
Hubei |
Anhui |
Guangxi |
Guangdong |
| seven |
Late ten days |
|
mature
|
mature |
mature |
mature |
mature |
| Mid day |
Maturity |
Maturity |
Maturity |
Maturity |
Maturity |
Maturity |
| six |
Late ten days |
Milk ripeness |
Heading |
Heading |
Heading |
Heading |
Milk ripeness |
| Mid day |
Heading |
Heading |
Booting |
Booting |
Heading |
Heading |
| Early ten days |
Booting |
Booting |
Tillering |
Tillering |
Booting |
Booting |
| five |
Late ten days |
|
Tillering
|
Tillering |
Tillering |
Tillering |
Tillering |
| Mid day |
Tillering |
Tillering |
Tillering |
Tillering |
tillering |
Tillering |
| Early ten days |
Tillering |
Rejuvenate |
Rejuvenate |
Transplanting |
Tillering |
Tillering |
|
4
|
Late ten days |
Rejuvenate |
Transplanting |
Emergence |
Emergence |
Tillering |
Tillering |
| Mid day |
Emergence |
Emergence |
Emergence |
Emergence |
raise rice seedlings |
Seedling raising |
| Early ten days |
Sowing |
Sowing |
|
|
Long leaf |
Long leaf |
|
3
|
Late ten days |
Sowing |
Sowing |
|
|
Emergence |
Emergence |
| Mid day |
|
|
|
|
Emergence |
Emergence |
| Early ten days |
|
|
|
|
sow |
Sowing |
Source: Agricultural time database of China Planting Information Network.
(4) Quality index of early indica rice
1. Quality index and grade of early indica rice
The quality indexes of early indica rice, late indica rice and indica glutinous rice include:
① Husked rice yield. The percentage of brown rice in the sample mass after net rice hulling, in which half of the imperfect grains are calculated.
② Head rice yield. Percentage of whole milled rice in the mass of net rice sample. The whole milled rice is the rice grain whose length reaches more than four fifths (including) of the average length of the whole rice grain when the brown rice is milled to the third grade (the first grade of the original rice standard) rice processing precision specified in GB 1354-1999 (the new national standard stipulates that the length reaches more than three fourths (including) of the average length of the whole rice grain).
③ Unsound kernel. It includes the following rice grains with edible value: immature grains: immature and plump grains, all of which are silty in appearance. Worm eaten grain: The grain eaten by insects and damaged the embryo and endosperm. Damaged grains: grains with disease on the surface of brown rice after hulling. Bud grain: a grain whose bud or young root has protruded from the rice hull, or whose bud or young root of brown rice has broken through the epidermis. Mouldy grains: Mouldy grains of rice grains, and mouldy grains on the surface of brown rice after shelling.
④ Out of grain brown rice: brown rice grains mixed in rice.
⑤ Mixed: other types of rice mixed in this type of rice.
⑥ Impurities: substances other than rice, including the following: 1. undersize: substances passing through a round sieve with a diameter of 2.0mm. 2、 Inorganic impurities: soil, sand, bricks and other inorganic substances. 3、 Organic impurities: rice grains, different kinds of grains and other organic substances without edible value.
⑦ Yellow grain rice: it is obviously yellow compared with the normal grain rice, or the chromaticity index b * value is not less than 20 under the 100 visual field of D65 illuminant.
⑧ Color and smell: the inherent comprehensive color, luster and smell of a batch of rice.
The current National Standard for Rice of the People's Republic of China (GB1350-1999) stipulates that all kinds of rice are divided into five grades according to the rate of roughness and the rate of head rice, and within grade rice must meet the requirements of the rate of head rice. The third grade is the medium quality standard and pricing basis, and 3% grade difference is applied for each grade. According to the national purchase policy, the price difference between adjacent grades of indica rice and japonica rice is 2 points/jin. Indica rice and japonica rice have the highest third grade, and 90% of them are above the third grade.
National Standard for Rice GB1350-1999 Quality Indexes of Early Indica Rice, Late Indica Rice and Indica Glutinous Rice
| Grade |
Roughness ratio,% |
Head rice rate,% |
Impurities,% |
Moisture,% |
Color and smell |
| one |
≥79.0 |
≥50.0 |
|
|
|
|
2
|
≥77.0 |
≥50.0 |
|
|
|
|
3
|
≥75.0 |
≥50.0 |
≤1.0 |
≤13.5 |
normal |
| four |
≥73.0 |
≥50.0 |
|
|
|
|
5
|
≥71.0 |
≥50.0 |
|
|
|
Note: The purchase of rice with moisture content greater than that specified in the table shall be subject to relevant national regulations.
2. Proper adjustment of quality indicators such as head rice rate
In the current national standard of "Rice", the head rice rate of indica rice regardless of grade is required to be no less than 50%. After the launch of the plan for the minimum purchase price of rice in 2005, the State Food Administration issued the Notice of the State Food Administration on Issues Related to the Implementation of National Standards in the Purchase of Early Indica Rice (Guo Liang Dian [2005] No. 15) in August, aiming at the phenomenon that water, impurities, head rice rate and other limiting indicators in some places failed to meet the national standards in the process of grain purchase in the main production areas of early indica rice in South China, If some limiting indicators in grain purchase fail to meet the requirements of national standards, the Regulations on Issues Related to the Implementation of Grain and Oil Quality Standards (Guo Liang Fa [2001] No.146) jointly issued by the former State Planning Commission, the State Food Administration and the General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine in November 2001 shall be implemented, and adjustments shall be made by deducting quantity and price. That is:
Moisture: if the actual moisture index is lower or higher than the standard specified index, based on the moisture index specified in the standard, the price will be increased by 0.75% for every 0.5 percentage point lower, and the price will be deducted by 0.3% and 0.75% for every 0.5 percentage point higher; If the price is lower or higher than 0.5%, no increase in price or amount will be calculated.
Impurities: if the actual impurity (or total impurity) index is lower or higher than the standard, based on the impurity (or total impurity) index specified in the standard, the price will be increased by 0.75% for every 0.5 percentage point lower, and the price will be reduced by 0.75% and the amount will be reduced by 0.75% for every 0.5 percentage point higher; If the price is lower or higher than 0.5%, no increase in price or amount will be calculated.
Head milled rice rate: based on the indicators specified in the standard, 0.75% will be deducted for every 1 percentage point lower, and no price will be deducted for less than 1 percentage point. If the price is higher than the standard, the price will not be increased. The head rice rate of early indica rice shall not be less than 44%.
According to the notice, the National Development and Reform Commission, the State Grain Administration and the National Standardization Administration jointly issued the Notice on Properly Adjusting the Control Indexes of the Whole Rice Rate of Early Indica Rice Purchase in 2005, requiring Jiangxi, Anhui, Hunan Hubei Province and China National Grain Reserve Management Corporation properly adjusted the control index of head milled rice rate of early indica rice in accordance with the Notice of the State Grain Administration on the Implementation of National Standards in the Purchase of Early indica Rice.
3. Revision of national standard for rice
In April 2007, the new national standard for rice, GB1350-XXXX (instead of GB1350-1999), reviewed by the State Grain and Oil Standardization Commission, stipulated unified quality indicators for early indica rice, late indica rice and indica glutinous rice. Since head rice rate is an important indicator for evaluating rice yield and quality, in order to give full play to the guiding role of standards for quality improvement and reflect the policy of high quality and good price, different requirements for head rice rate are set for different grades of rice, with 50%, 47%, 44%, 41% and 38% for indica rice grades 1-5.
Newly revised national standard for rice GB1350-XXXX (replacing GB1350 - 1999) (to be issued and implemented)
Quality index of early indica rice, late indica rice and indica glutinous rice
|
Grade
|
Roughness ratio/(%) |
Head milled rice rate/(%) |
Impurities/(%) |
Moisture/(%) |
Yellow rice/(%) |
Out of grain brown rice/(%) |
Mixed/(%) |
Color and smell |
| one |
≥79.0 |
≥50.0 |
≤1.0 |
≤13.5 |
≤1.0 |
≤2.0 |
≤5.0 |
normal |
| two |
≥77.0 |
≥47.0 |
| three |
≥75.0 |
≥44.0 |
| four |
≥73.0 |
≥41.0 |
| five |
≥71.0 |
≥38.0 |
| Out of equality |
<71.0 |
- |
Note: "-" means not required
(5) Storage of early indica rice
The rice grain has complete inner and outer glumes, which protects the endosperm part easy to deteriorate, and has a certain resistance to insects, mold, moisture and heat, and the water content of the inner and outer glumes of the rice grain is lower than that of the rice grain. These characteristics make rice relatively easy to store.
As the fat (oil) content is less than that of mid late indica rice, and the aging speed is slow, early indica rice is the most tolerant variety in rice storage, so it has become an important reserve variety of grain reserves at all levels. The storage life of early indica rice in the south of the Yangtze River is usually three years, and that of some provinces such as Guangdong is two years. Six measures are usually taken for early indica rice from storage to storage: control of moisture, removal of impurities, classified storage, ventilation and cooling, control of pests, and sealing of grain piles. The tall bungalow warehouses storing rice are equipped with circulating fumigation, mechanical ventilation and refrigeration equipment.
(6) Economic and Social Significance of Early Indica Rice
1. Early indica rice is the first major grain crop planted and harvested in the same year. Therefore, the production of early indica rice has become the touchstone of whether national policies support grain production and farmers' enthusiasm for grain planting.
2. Fluctuations in early indica rice production directly affect late rice production, and thus affect rice production throughout the year. According to relevant research, the correlation coefficient between the planting area of early indica rice and late rice reached 0.93 between 1994 and 2005.
3. Early indica rice is the most important commodity food source in the southern rice region, because its marketability is better than other rice crops. Due to the poor palatability of early indica rice as edible rice, farmers generally sell most of them as commercial grain, except for keeping some as a supplement to rations and feed grains. Moreover, with the increase in the number of migrant workers and the change in the way farmers store grain in recent years, the commodity volume of early indica rice is still increasing. Therefore, the commodity rate of early indica rice is relatively high, about 50-60%.
4. Early indica rice is the main grain reserve. As early indica rice is more tolerant to storage than mid late indica rice and is the first rice variety to be listed in the market, the grain department of the southern region will regard early indica rice as the main rice variety for reserve grain rotation. From the practice in recent years, local policy reserve demand has become an important way out for early indica rice, especially for the new grain listed that year. Local policy reserve demand has become the most important factor determining the purchase price and even the market sales price trend in the short term.
5. Early indica rice is one of the basic guarantees for most farmers in South China. The rice producing areas in South China involve nearly 400 million farmers in 13 provinces. Early indica rice is a part of their rations and also the main economic source of farmers in the main rice producing areas, accounting for a large share. From the perspective of comprehensive benefits, the planting cost of early indica rice is relatively low compared with other crops, the yield is relatively stable, the health quality is also good, and the natural risk is relatively small. Therefore, early indica rice plays an important role in stabilizing and increasing the income of rice farmers.
6. In the long run, early indica rice is an important support for food security in China. As far as the current grain production capacity is concerned, no matter the planting area or yield of early indica rice, other varieties are difficult to supplement or replace. Without this piece, food security will inevitably be threatened.

