Key points of transaction rules
Futures trading refers to the trading activities of buying and selling certain futures contracts in a futures exchange.
1. The transaction price is the price formed by the computer automatic matching system of the Exchange, which orders the purchase and sale orders in the principle of price priority and time priority. When the buying price is greater than or equal to the selling price, the transaction price is automatically matched. The combined transaction price is equal to the middle of the buying price, the selling price and the previous transaction price.
2. Trading orders are divided into price limit orders, cancellation orders and other orders specified by the Exchange. The maximum order quantity of a price limit order is 500 orders each time, and the minimum order quantity of a trading order is 1 order each time. The quotation of a trading order can only be within the price fluctuation limit.
3. The Exchange shall implement a transaction code filing system. Transaction code refers to the special code for members and clients to conduct futures transactions, including the transaction code of non futures company members and the transaction code of clients.
4. The Exchange provides members, customers and the public with futures trading information on an immediate, daily, weekly, monthly and annual basis.
Key points of settlement rules
Settlement refers to the business activities of calculating and allocating the trading deposits, profits and losses, service charges, payment for delivery of goods and other relevant funds of members according to the trading results and relevant regulations of the Exchange.
1. The Exchange shall open a special settlement account in each depository bank for depositing members' deposits and related funds. Members shall open a special capital account in the depository bank for deposit of deposits and related funds. The exchange of funds for futures business between the Exchange and members shall be handled through the special settlement account of the Exchange and the special fund account of members.
2. The Exchange shall implement separate account management for the deposits of members in the special settlement account of the Exchange, set up a subsidiary account for each member, and register and calculate the deposits and withdrawals, profits and losses, trading deposits, service fees, etc. of each member in chronological order. The members of the futures company shall implement separate account management for the deposits of customers into the special fund account of the members, set up a subsidiary account for each customer, and register and calculate the deposits, profits and losses, trading deposits, service fees, etc. of each customer in chronological order.
3. The Exchange adopts a margin system. The margin is divided into settlement reserve and transaction margin. The settlement reserve refers to the funds that members have prepared in advance in the special settlement account of the exchange for transaction settlement, and is the margin not occupied by the contract. Trading margin refers to the funds deposited by members in the special settlement account of the Exchange to ensure the performance of the contract, which is the margin occupied by the contract.
4. The Exchange shall implement a liability free settlement system on the same day. The day debt free settlement system means that after the end of each day's trading, the Exchange settles the profit and loss, trading margin, service charges, taxes and other expenses of all contracts at the settlement price of the day, transfers the net amount of the accounts receivable and payable at one time, and increases or decreases the settlement reserves of members accordingly.
5. At the end of the daily closing, if the settlement reserve after settlement is less than the minimum balance, the member must make up the funds to the minimum balance of the settlement reserve before the opening of the next trading day. If it fails to make up in time, if the balance of the settlement reserve is greater than zero but lower than the minimum balance of the settlement reserve, it is prohibited to open new positions; If the balance of the settlement reserve is less than zero, the Exchange will implement "forced closing" in accordance with the relevant risk control management regulations.
Key points of settlement rules
Physical delivery refers to the process that when a futures contract expires, the trading parties settle the outstanding position contract by transferring the ownership of the commodity contained in the contract.
1. After the last trading day of the contract, the holders of all open positions shall perform the contract by physical delivery. The physical delivery of clients shall be handled by the members, and shall be carried out in the name of the members at the Exchange. Natural person customers shall not gold Physical delivery. After the closing of the third trading day before the last trading day of the gold futures contract, the position of the natural person customer in the gold futures contract shall be zero.
2. The first delivery date of the delivery procedure: the seller delivers the standard warehouse receipt. The Seller shall deliver the valid standard warehouse receipt that has paid the storage fees (paid to the fifth delivery date, including the fifth delivery date) to the Exchange. The second delivery date: the Exchange allocates standard warehouse receipts. The third delivery date: the buyer must pay for the goods and obtain the standard warehouse receipt before 14:00 on the third delivery date; The seller shall collect the payment, and the exchange shall pay the payment to the seller before 16:00 on the third delivery day. Fourth and fifth delivery date: the seller submits the invoice.
3. Circulation procedures for physical delivery of standard warehouse receipts at the exchange:
(1) The seller's customer authorizes the standard warehouse receipt to the seller's member to handle the physical delivery business;
(2) The seller member delivers the standard warehouse receipt to the Exchange;
(3) The Exchange shall distribute the standard warehouse receipt to the buyer members;
(4) The buyer member distributes the standard warehouse receipt to the buyer customer;
4. Receipt and issue
(1) Before delivering goods to the designated delivery vault, the owner of the goods shall handle warehousing declaration (delivery forecast). The contents of warehousing declaration include variety, grade, quantity, delivery unit and proposed delivery place. Customers' declaration shall be handled through the members entrusted by them.
(2) The Exchange shall designate the owner to pay the vault within 3 trading days, taking into account the wishes of the owner, if the storage capacity allows. The owner of the goods shall deliver goods to the designated delivery vault identified in the approved warehousing declaration within the validity period specified by the Exchange. Gold ingots that have not been approved by the Exchange to be warehoused or warehoused within the specified validity period cannot be used for delivery.
(3) After the gold ingots arrive at the designated delivery vault, the designated delivery vault shall inspect and review the gold ingots and relevant documents according to relevant regulations. Inspection is divided into quality inspection and quantity (quality) inspection. When warehousing, the owner of the goods shall supervise the receipt in the designated delivery vault; If the owner of the goods fails to arrive at the warehouse to supervise the receipt, it shall be deemed that the owner of the goods agrees to designate the inspection result of the delivery vault.
(4) After the gold ingots are warehoused and accepted as qualified, the members shall submit the application for making standard warehouse receipts to the Exchange, and the Exchange shall notify the designated delivery vault to issue standard warehouse receipts in the standard warehouse receipt management system after the application is reviewed as qualified.
(5) When picking up the goods, the consignor shall submit the outbound application through the standard warehouse receipt system and select the place of picking up. The Exchange shall make overall arrangements for the picking up vault within the picking up place selected by the consignor, and determine one of the trading days as the delivery date within five working days after the consignor submits the picking up application. On a certain trading day before the delivery date, the Exchange will notify the owner of the delivery date through the standard warehouse receipt management system, and change the trading day to the delivery notice day. The owner of the goods should withdraw money from the warehouse within two working days from the delivery date.
When the designated delivery vault delivers goods, it shall timely fill out the Standard Warehouse Receipt Delivery Confirmation Form (in duplicate, with the owner and the designated delivery vault holding one copy respectively), and properly keep it for future reference.
5. Settlement of delivery, settlement of excess and shortage of receipt and delivery, and invoice process
(1) The difference between the net weight of gold ingots in each warehouse receipt and the standard weight of the warehouse receipt (net weight) when depositing or withdrawing gold ingots is excessive or insufficient. If the difference is positive, it is called positive overflow short; if the difference is negative, it is called negative overflow short. The Exchange shall respectively settle the surplus and shortage on the surplus and shortage settlement date (i.e. the effective date of the warehouse receipt when gold ingots are put into storage or the delivery notice date when gold ingots are put out of storage). The special invoice for gold settlement refers to the ordinary invoice (including invoice copy, settlement copy and counterfoil copy) printed with the approval of the competent tax authority and specially used for gold settlement and surplus/shortage settlement.
(2) Gold delivery, settlement and invoice process
① Delivery and settlement of gold futures: the delivery and settlement price of gold futures is the weighted average price of the last five trading days of the contract according to the trading volume. At the time of settlement, the Buyer and the Seller shall settle according to the settlement price of the contract.
② Settlement of payment for goods delivered: the payment for goods delivered by the buyer and the seller shall be settled according to the standard weight (pure weight) of the warehouse receipt. The Exchange only settles for members. The payment for goods of the buyer's customer must be transferred through the buyer's member, and the payment for goods of the seller's customer must be transferred through the seller's member.
③ Delivery invoice: common invoice shall be issued uniformly at the time of delivery.
④ Transfer of delivery invoice: the seller's non futures company member or customer issues a common invoice to the exchange, the exchange issues the Special Invoice for Gold Settlement (invoice copy) to the buyer's non futures company member or customer, and provides the seller's non futures company member or customer with the Special Invoice for Gold Settlement (settlement copy) and the Special Invoice for Gold Settlement The stub copy of shall be kept by the Exchange.
⑤ Invoices and receipts between customers and the Exchange must be transferred through the member units.
(3) Gold warehousing surplus/shortage settlement and invoice process
① Settlement of excess and short receipt: the excess and short receipt of gold shall be settled at the settlement price of the gold futures contract in the latest month listed on the exchange on the trading day before the excess and short settlement day.
② Bills related to surplus and shortage: the gold deposit enterprise shall issue a common invoice to the exchange for the surplus and shortage; The Exchange shall issue the Special Invoice for Gold Settlement (invoice copy) to the gold depositor, and the counterfoil copy and settlement copy of the Special Invoice for Gold Settlement shall be retained by the Exchange.
③ The calculation formula of the surplus/shortage settlement payment for goods: surplus/shortage settlement payment for goods=surplus/shortage × settlement price of the gold futures contract of the latest month listed on the exchange on the trading day before the surplus/shortage settlement day.
(4) Gold outbound surplus/shortage settlement and invoice process
① Delivery of standard warehouse receipt without delivery Overdelivery and short settlement: when a member or customer (the consignee) takes delivery of standard warehouse receipt without delivery, the excess and short settlement shall be based on the settlement price of the gold futures contract of the latest month listed on the exchange on the trading day before the settlement day of excess and short. The Exchange shall issue the Special Invoice for Gold Settlement (invoice copy) to the consignee for the positive and negative balance, and the counterfoil copy and settlement copy of the Special Invoice for Gold Settlement shall be retained by the Exchange; The pick up party shall issue an ordinary invoice to the exchange for the negative excess short.
② Delivery of standard warehouse receipts held through settlement settlement of surplus and shortage: when members or customers deliver the standard warehouse receipts held through settlement, the surplus and shortage shall be settled according to the settlement price of gold futures contracts of the latest month listed for trading on the trading day before the settlement day of surplus and shortage, and the competent tax authority of the exchange shall, according to the Delivery Settlement Form provided by the buyer members or customers The Standard Warehouse Receipt Delivery Confirmation Sheet and the Surplus/Shortage Settlement Sheet shall issue special VAT invoices (deduction sheets) to the buyer members or customers on behalf of the Exchange according to the actual delivery payment (consisting of delivery payment and surplus/shortage settlement payment) and the quantity of goods picked. The invoice issuing and accounting sheets of the special VAT invoices shall be retained by the transaction. If the member unit or customer of the consignee is a non VAT general taxpayer, no VAT special invoice will be issued.
③ The calculation formula of the surplus/shortage settlement payment for goods: surplus/shortage settlement payment for goods=surplus/shortage × settlement price of the gold futures contract of the latest month listed on the exchange on the trading day before the surplus/shortage settlement day.
(5) The actual delivery payment when the buyer member or customer picks up the goods and leaves the warehouse is composed of the delivery payment and the surplus/shortage settlement payment, of which the delivery payment is determined according to the last in, first out principle.
Key points of risk management system
margin system
The Exchange implements the trading margin system. The minimum trading margin of gold futures contracts is 7% of the contract value.
The Exchange shall adjust the trading margin according to the different amount of gold futures contract positions, and the adjustment method is as follows:
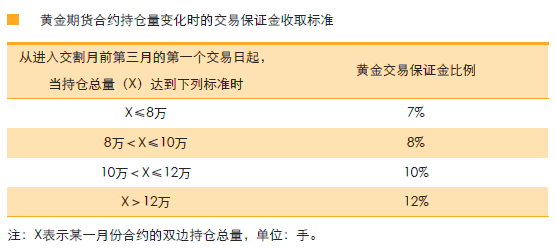
During the trading process, when the position of a gold futures contract reaches the total position of a certain level, the collection standard of trading margin will not be adjusted temporarily. At the settlement of the day, if the position of a gold futures contract reaches the total position of a certain level, the Exchange will charge the trading margin corresponding to the total position of all positions of the contract. If the margin is insufficient, it shall be added in place before the opening of the next trading day.
The Exchange adjusts the trading margin according to the different stages of the listing operation of the futures contract (that is, from the date of the new listing of the contract to the last trading day), and the adjustment method is as follows:

If two or more kinds of trading margin ratios are applicable to the relevant provisions of the Exchange at the same time, the trading margin shall be charged at the highest value of the prescribed trading margin ratios.
When the gold futures contract reaches the standard that the trading margin should be adjusted, the Exchange shall settle all historical positions of the contract according to the new trading margin standard at the time of settlement on the trading day before the implementation of the new standard. If the margin is insufficient, it shall be added in place before the opening of the next trading day. After entering the delivery month, the seller can use the standard warehouse receipt as the performance guarantee for the futures contract position in the delivery month with the same quantity as that shown, and the trading margin corresponding to its position will not be collected.
Limited warehouse system
The term "position limitation" refers to the maximum amount of a certain contractual speculative position that can be held by members or clients unilaterally calculated according to the provisions of the Exchange.
The specific provisions on the position limit ratio and position limit of gold futures contracts of members of futures companies, non members of futures companies and customers in different periods are as follows:
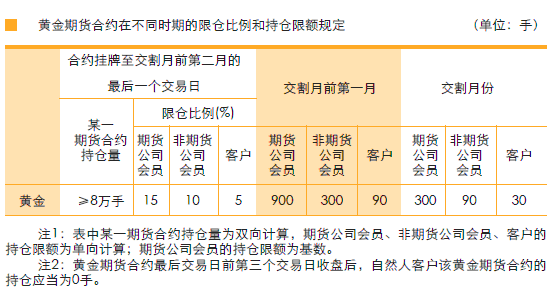
The same customer has opened multiple transaction codes at different futures company members, and the total of all positions on each transaction code shall not exceed the position limit of one customer. Before the closing of the last trading day of the first month before the delivery month, the positions of each member and each customer in each member's gold futures contract shall be adjusted to an integral multiple of three hands. After entering the delivery month, the positions of members and customers in gold futures contracts shall be integral multiples of three hands, and the positions newly opened and closed shall also be integral multiples of three hands; After the closing of the third trading day before the last trading day of the gold futures contract, the position of the natural person customer in the gold futures contract shall be zero.
price limit
The Exchange implements the price limit system, and the Exchange formulates the maximum daily price fluctuation range of each listed futures contract. In the trading process of gold futures contracts, when the following situations occur, the Exchange can adjust the limit range of the rise and fall according to the market risk:
(1) When the price of a futures contract continues to rise or fall in the same direction;
(2) In case of national statutory long holidays;
(3) When the Exchange considers that the market risk changes significantly;
(4) Other circumstances deemed necessary by the Exchange. If two or more kinds of price limits are applicable to the relevant provisions of the Exchange at the same time, the price limit shall be determined according to the highest value of the stipulated price limit.
When the cumulative increase or decrease of a gold futures contract reaches 10% for three consecutive trading days; Or the cumulative increase or decrease for four consecutive trading days reached 12%; Or when the cumulative increase or decrease for five consecutive trading days has reached 14%, the Exchange may, according to the market situation, unilaterally or bilaterally, with the same or different proportion, increase the trading margin of some members or all members, restrict some or all members to make cash payments, suspend some or all members to open new positions, adjust the limit of increase or decrease, and close positions within a time limit, One or more of the measures such as compulsory position closing, but the adjusted range of the limit of rise and fall shall not exceed 20%.
When there is no continuous quotation on one side of a gold contract in the same direction, the Exchange will take corresponding measures in accordance with the Shanghai Futures Exchange Risk Control Management Measures and other relevant provisions.

Large household reporting system
When the speculative position of a member or client in a certain type of position contract reaches more than 80% (including this amount) of the speculative position limit specified by the Exchange, the member or client shall report its capital situation and position to the Exchange, and the client shall report through the members of the futures company. The Exchange may formulate and adjust position reporting standards according to market risk conditions.
Compulsory position closing system
Compulsory position closing refers to a compulsory measure taken by the Exchange to close the positions of members and customers when they break the rules. When a member or client has one of the following circumstances, the Exchange will forcibly close its position:
(1) The balance of the member's settlement reserve fund is less than zero and cannot be replenished within the specified time limit;
(2) The position exceeds the position limit;
(3) The position is not adjusted to the corresponding integral multiple within the specified time as required;
(4) Being punished by the Exchange for compulsory position closing due to violation of regulations;
(5) The position should be closed compulsorily according to the emergency measures of the Exchange;
(6) Other positions that should be closed by force.
Risk warning system
When the Exchange deems it necessary, it may separately or simultaneously take one or more of the measures required to report the situation, talk about reminding, written warning, public censure, and release risk warning announcements to warn and resolve risks.
Key points of hedging rules
1. The application for gold hedging position shall be submitted before the 20th day of the month before the delivery month of the hedging contract, and the overdue exchange will no longer accept the application for hedging of the contract in the delivery month. The hedger can apply for the hedging amount of contracts in multiple delivery months at one time.
2. Traders who have been approved for hedging transactions shall establish positions according to the approved trading positions and limits within the position establishment period approved by the Exchange (no later than the last trading day of the month before the delivery month of the hedging contract). If a position is not established within the specified time limit, it shall be deemed that the hedging trading quota is automatically waived.
3. The hedging amount shall not be reused from the first trading day of the month before the month of closing.




