Futures investment skills
(10) , magic numbers and waves
① , Overview
It is often said that ten analysts have eleven wave counting methods. Most people think that Eliot's wave theory is too abstruse to grasp. In 1946, Eliot completed his masterpiece on wave theory, The Law of Nature -- The Secret of the Universe. Look! What is his boldness. Eliot firmly believes that his wave theory is part of the universal natural law that restricts all human activities. The advantage of wave theory is that it can send warning signals in advance for the upcoming top or bottom, while the traditional technical analysis methods can only be verified afterwards.
Eliot believes that the fluctuation of both stock and commodity prices is the same as the tide and wave of nature, one wave follows another, which has a considerable degree of regularity, showing the characteristics of cyclical cycles, and any fluctuation has traces.
Therefore, investors can predict the future trend of the price according to these regular fluctuations, and apply the buying and selling strategy. Eliot's wave theory has a comprehensive perspective on market operation, which helps to explain why specific forms appear, where they appear, and why they have such predictive significance. In addition, it also helps us to judge the position of the current market in its overall cycle structure.
The mathematical basis of wave theory is a series of numbers discovered by Fibonacci in the 13th century. Fibonacci series is also the mathematical basis of the golden section, golden rectangle and logarithmic spiral, which have their shadow in music, art and architecture.
② Basic principles of Eliot's wave theory
The wave theory has three important aspects -- shape, proportion and time, and its importance follows the above order. The so-called form refers to the form or structure of waves, which is the most important part of wave theory. Proportional analysis refers to determining the withdrawal point and price target by measuring the relationship between waves. The last aspect is time. The waves are also related in time. We can use this relationship to verify the wave shape and proportion.
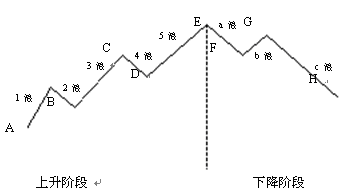
Eliot's theory is mainly applied to stock index, especially Dow? Jones Industrial Stock Index. In the most basic form of wave theory, the stock market follows a cyclical rhythm, first rising in five waves and then falling in three waves.
As shown in the figure below, it is a complete cycle. Count the number of waves, then a complete cycle includes 8 waves - 5 waves rise, 3 waves fall. In the rising phase of the cycle, each wave is numbered. Wave 1, wave 3 and wave 5 are rising waves, which are called main waves, while the direction of wave 2 and wave 4 is opposite to the rising trend. Because wave 2 and wave 4 are respectively the adjustment of wave 1 and wave 3, they are called adjustment waves. After the completion of the above five waves, there is an adjustment in the form of three waves. The three waves are represented by the letters a, b and c.
③ Fibonacci series is the mathematical basis of wave theory
Eliot said in his Law of Nature that the mathematical basis of wave theory is a series of numbers discovered by Fibonacci in the 13th century. This sequence was later named after its discoverer, and is generally called Fibonacci sequence (or Fibonacci number). In the Book of Calculations, Fibonacci series appeared for the first time as a solution to the mathematical problem of rabbit breeding. This series of numbers is 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89144, and so on, to infinity.
④ Fibonacci ratio and price rollback
Wave theory consists of three aspects -- wave shape, ratio and time.
The basic wave structures are organized according to Fibonacci series. A complete cycle consists of 8 waves, of which 5 waves rise and 3 waves fall -- these are Fibonacci numbers. Then subdivide into the following two levels to get 34 waves and 144 waves respectively -- they are also Fibonacci numbers. However, the application of Fibonacci series in wave theory is not only about counting waves, but also about the relationship between waves. Here are some of the most commonly used Fibonacci ratios:
1. Only one of the three main waves extends, and the other two have the same time and amplitude. If 5 waves extend, then 1 wave and 3 waves are roughly equal; if 3 waves extend, then 1 wave and 5 waves tend to be the same.
2. Multiply 1 wave by 1.618, and then add it to the bottom of 2 waves to get the minimum target of 3 waves.
3. Multiply 1 wave by 3.236 (=2 * 1.618), and then add it to the top and bottom of 1 wave respectively, which is roughly the maximum and minimum target of 5 waves.
4. If 1 wave and 3 waves are roughly equal, we expect 5 waves to extend. The estimation method of its price target is to measure the distance from the bottom of wave 1 to the top of wave 3, multiply it by 1.618, and finally add the result to the bottom of wave 4.
5. In the adjustment wave, if it is the usual 5-3-5 saw adjustment, then the length of wave c is often equal to that of wave a.
6. Another way to estimate the length of wave c is to multiply the length of wave a by 0.618, and then subtract the product from the bottom point of wave a.
7. In the case of 3-3-5 platform shape adjustment, wave b may reach or exceed the peak of wave a, so the length of wave b is about 1.618 times the length of wave a.
8. In a symmetrical triangle, each subsequent wave is approximately 0.618 times the previous one.
⑤ , Fibonacci percentage rollback
Through percentage rollback, we can estimate the price target. In the fallback analysis, the most commonly used percentages are 61.8% (usually approximately 62%), 38% and 50%. The market usually retreats according to a certain predictable percentage -- the most familiar ones are 33%, 50% and 67%. Fibonacci series slightly adjusts the above figures. Under the strong trend, the minimum retracement was around 38%. In a fragile trend, the maximum rollback percentage is usually 62%.
As we said earlier, in the Fibonacci sequence, except for the first four numbers, the Fibonacci ratio tends to 0.618. The first three ratios are 1/1 (100%), 1/2 (50%), and 2/3 (67%). Many people did not know before learning Eliot's theory that the 50% retracement that they are familiar with is actually a Fibonacci ratio. The same is true for two thirds of retreats and one third of retreats, which mark important support or blocking areas.
⑥ Three aspects of integrated wave theory
The ideal situation is that the three aspects of wave shape, ratio analysis and time target coincide. For example, the wave analysis shows that the fifth wave has been completed; And the 5 waves have reached 1.618 times the distance from the bottom point of 1 wave to the top point of 3 waves; At the same time, from the starting point of this trend (the previous trough) to now, it is exactly 13 weeks, and from the previous peak to now, it is exactly 34 weeks. Then, we are very sure that an important top of the market is coming.
The research results of stock and futures market charts show that there are many kinds of Fibonacci time relations. However, the first problem is that we have too many choices. We can calculate the Fibonacci time target from top to top, from top to bottom, from bottom to bottom, from bottom to top, etc. Unfortunately, we can always confirm these relationships afterwards. In many cases, we don't know which relationship is suitable for the current situation.

