Flow and solute transport simulation software PC Progress HYDRAS 2D/3D Pro 2.04.0580
HYDROUS is an environmental simulation software running under Windows system, which is mainly used for water flow and solute transport in variable saturated porous media. HYDROUS includes 2D and 3D finite element calculations for simulating water, heat and multi solute transport in variable saturated porous media, including a parameter optimization algorithm for inverse estimation of water pressure and solute transport parameters of various soils. The interactive graphical interface of the model enables data pre-processing, structured and unstructured finite element mesh generation and graphical display of results.
There are five versions of HYDRAS, and users can choose the most suitable version. Users can select 2D applications limited to general functions (2D Standard version, consistent with the previous Hydras-2D function with MeshGen-2D) or 2D and 3D applications (such as 3D Standard or 3D Professional). Users can also choose relatively simple (2D rectangular geometry - 3D Lite, which is consistent with the Hydrus-2D function without MeshGen-2D) or 3D geometric solid - 3D Lite) or more complex geometry (2D Standard for ordinary 2D geometry, 3D Standard based on 2D and layered 3D, and 3D Professional for ordinary 3D geometry). Users can also choose to upgrade from a lower version to a higher version.
Standard calculation model
HYDROUS is a finite element calculation model that simulates the two-dimensional and three-dimensional movement of water, heat and multi solute in variable saturated porous media. HYDRUS numerically solves Richards equation of saturated unsaturated flow and convection diffusion equation of heat transfer and solute transport.
The flow equation includes a sinking period, which can lead to the absorption of water by plant roots. The heat transfer equation considers the flow conduction and convection. The management of convection diffusion solute transport equation is a very common form, including the provisions of nonlinear non-equilibrium reaction of solid and liquid and linear equilibrium reaction of liquid and gas. Therefore, both adsorbed solutes and volatile solutes (such as pesticides) have been considered. The solute transport equation also includes the influence of zero order production, independent first-order degradation of other solutes, first-order attenuation and production reaction, so as to provide the coupling required between solutes in the continuous first-order chain. Migration simulation will also cause liquid convection and diffusion, and gas diffusion, so the sub model can simulate solute migration at the same time under liquid and gas conditions. At present, up to 15 kinds of solutes can be considered in HYDRAS, which are coupled in a one-way chain or transported independently between solutes. Physical nonequilibrium solute transport is caused by dual zone and dual pore formulas, and the liquid phase is divided into mobile and immovable regions. Adhesion and separation theory, including filtration theory, and simulation of virus, colloid and bacterial migration are also included.
HYDROUS can be used to analyze the movement of water quality and solute in unsaturated, partially saturated or saturated porous media. HYDRUS can treat the flow area by irregular boundary, and the flow area itself may be composed of non-uniform soil with local anisotropy of any degree. Water flow and migration may occur in vertical plane or horizontal plane, vertical axis or three-dimensional area with radial symmetry.
The flow part of the model can be used to deal with continuous or time-varying specified direction and flow boundaries, as well as the boundaries controlled by meteorological conditions. The soil surface boundary conditions may change during the simulation from a given flow to a specified direction type condition, and vice versa. It can also deal with the free surface boundary through the residual water volume of the saturated part of the water area and the undrained boundary conditions. Node drainage is represented by a simple simulated experimental relationship.
For solute transport, the software supports both continuous and variable specified concentrations (Dirichlet or first type) and concentration flux boundaries (Cauchy or third type). The diffusion tensor includes the molecular diffusion and the tortuous effect of the resultant reaction.
Hydrological properties of unsaturated soil are summarized by the following theories: van Genuchten in 1980, Brooks and Corey in 1964, Durner in 1994, Kosugi in 1995, and modified van Genuchten's type analytic function. These amendments further describe the hydraulic properties near saturation. HYDRUS software includes the hysteresis combined with empirical simulation introduced by Scott et al. in 1983 and Kool and Parker in 1987.
This model assumes that the drying sweep curve is derived from the main drying curve and the wetting sweep curve is derived from the main wetting curve. HYDRUS also includes the hysteresis model of Lenhard detal. in 1991 and Lenhard and Parker in 1992, which eliminates the pump by tracking the historical reversal point. HYDRUS can implement scaling process in a given soil environment to achieve approximate hydraulic change. Through a set of linear scale change tools, it involves the relationship between individual soil hydraulic characteristics and reference soil.
The governing equations are solved using Galerkin's linear finite element method applied to the triangular element network. The saturated and unsaturated states are realized by the integration of finite difference schemes. Results The equation is solved iteratively, through linearization and subsequent Gaussian elimination method, the conjugate gradient method for banded matrix and symmetric matrix or the orthogonal minimization method for asymmetric matrix. Additional measures are taken to improve the efficiency of solving transient problems, including automatic time step adjustment and ensuring that Courant and Peclet numbers do not exceed preset levels. Use the mass conservation method proposed by Celiaetal. in 1990 to evaluate the water content. Reducing the upward weight of numerical oscillation is included as an option to solve the migration equation.
In addition, HYDRUS can perform Marquardt Levenberg type parameter estimation techniques to perform hydraulic inverse estimation or solute transport for selected soils and measure transient or steady-state flow and transport data (only in 2D version). This process allows the estimation of several unknown parameters, such as the observed water content, pressure head, concentration or instantaneous or cumulative boundary flux (such as infiltration or outflow data). Additional reserved or hydraulic conductivity data and parameter compensation function of constrained optimization. The parameters of constrained optimization are kept in the feasible region (Bayesian estimation) and can be included in the parameter estimation process.
A new module to simulate the biochemical transformation and degradation process of groundwater flow constructed wetland was developed for the two-dimensional application of HYDRAS (Langergraber and Simunek in 2005, Langergraberetal in 2009).
This module believes that a large number of physical, chemical and biological processes are active in wetlands, including three components of organic substances (easy to degrade, slowly biodegradable and inert) in biochemical degradation and transformation processes, four nitrogen compounds (ammonium, nitrite, nitrate, and double nitrogen), inorganic phosphorus, heterotrophic and autotrophic microorganisms, dissolved oxygen and/or sulfur, which are active at the same time and affect each other.
Add ons
UNSATCHem module is mainly used to simulate migration and reaction of main ions. UNSATCHEM module simulates the migration of major ions (such as calcium, magnesium, sodium, potassium, SO4, carbonate gas and Cl) in variable saturated porous media, including the equilibrium and non-equilibrium chemical reaction kinetics of major ions. The generated code can be used to predict the main ion chemistry, water and solute flux of soil in transient flow.
The Wetlands module is used to simulate the reaction of constructed wetlands. The design of constructed wetland water treatment system can optimize the treatment process found in the natural environment. The HYDRAS wetland module includes two biokinetic model formulas. In the original wetland CW2D module, the conversion and degradation processes of organic matter, nitrogen and phosphorus in aerobic and anoxic processes were considered, as well as the organic matter, nitrogen and sulfur in aerobic, anoxic and anaerobic processes in the new CWM1 module.
DualPerm module (version 2.02 and above) is used to simulate two-dimensional variable saturated water movement and solute transport in dual permeability porous media, that is, preferential and non-equilibrium water and solute transport.
The C-Ride module (version 2.02 and above) is used to simulate the solute transport of two-dimensional colloids (such as heavy metals, radionuclides, pharmaceuticals, pesticides, explosives) that strongly adsorb pollutants. It is mainly associated with solid phases, which are generally considered static, but can also adsorb mobile colloidal particles (such as microorganisms, humus substances, suspended clay particles, and metal oxides), It can be used as the carrier of pollutants, thus providing a rapid migration path for these pollutants.
HP2 module (version 2.02 and above) integrates HYDROUS (its two-dimensional part) and PHREEQC geochemical code [Parkhurst and Appelo in 1999] to develop this new integrated simulation tool (HP2-HYDROUS-PHREEQC-2D abbreviation), which is mainly different from a similar one-dimensional module HP1. This module can consider various hybrid equilibrium/dynamic biogeochemical reactions.
HYPAR is a parallel version of the standard 2D and 3D HYDRAS computing module. (h2d_calc.exe and h3d_calc.exe)
HYPAR uses parallel computing tools and technologies to effectively take advantage of multi-core and multiprocessor computers and significantly speed up time-consuming simulations, especially those that require a large number of finite elements
The purpose of the Slope Classic add-on module is mainly to check the stability of embankments, dams, cut earth and fix baffle structures. The influence of water modeling uses the distribution of pore pressure, which is the result of the inlet automatically assigned time from Hydra. The water distribution of each time step can be analyzed separately.
The SLOPE Cube (Slope Stress and Stability) accessory module was jointly developed by Dr. Ning Lu of Colorado University of Mining and Technology. It uses a unified effective stress method for saturated and unsaturated conditions. The purpose of this module is to predict the initiation of infiltrating induced landslide and carry out slope stability analysis under variable saturated soil conditions.
graphical user interface
An output requirement for running HYDRAS based on Microsoft Windows graphical user interface (GUI) management, as well as grid design and editing, parameter configuration, problem execution and result visualization. HYDRAS also includes a set of controls that allow users to create a flow and migration model and analyze the running graphics. Use space and cross section views and line graphs to check input and output. The main program unit of the HYDRUS GUI defines the overall computing environment of the system. This main module controls the execution of the program and determines which other optional tools are necessary. The module also contains a project manager and two preprocessing and post-processing units. The pretreatment unit includes all necessary parameter specifications, such as successfully running the HYDRUSFORTRAN language code, relatively simple grid generators in rectangular and hexahedral transmission domains, grid generators in complex 2D and 3D domains for unstructured finite element meshes, soil hydraulic properties of a small directory and generating soil hydraulic properties from RosettaLite program of soil structure data.
Automatic generation of finite element mesh
Data pre-processing involves the specification of two-dimensional flow regions, with arbitrarily shaped continuous polylines, arcs, splines, discretization of domain boundaries, and the next version of an unstructured finite element mesh. HYDRAS (standard version) has an optional mesh generation program, Meshgen can generate a two-dimensional domain of unstructured finite element mesh. Based on Delaunay's inference, HYDROUS has been seamlessly integrated into the HYDROUS environment. Without the Meshgen program, the HYDRAGUI provides a simple, structured grid automatic construction option (Lite version). The 3D version adds the specified number of layers with the same or different thickness under the Lite and Standard versions. HYDRUS3D Professional Edition has a 3D mesh generation program (GENEX and T3D) to generate unstructured finite element meshes for general 3D domains.
Post processing
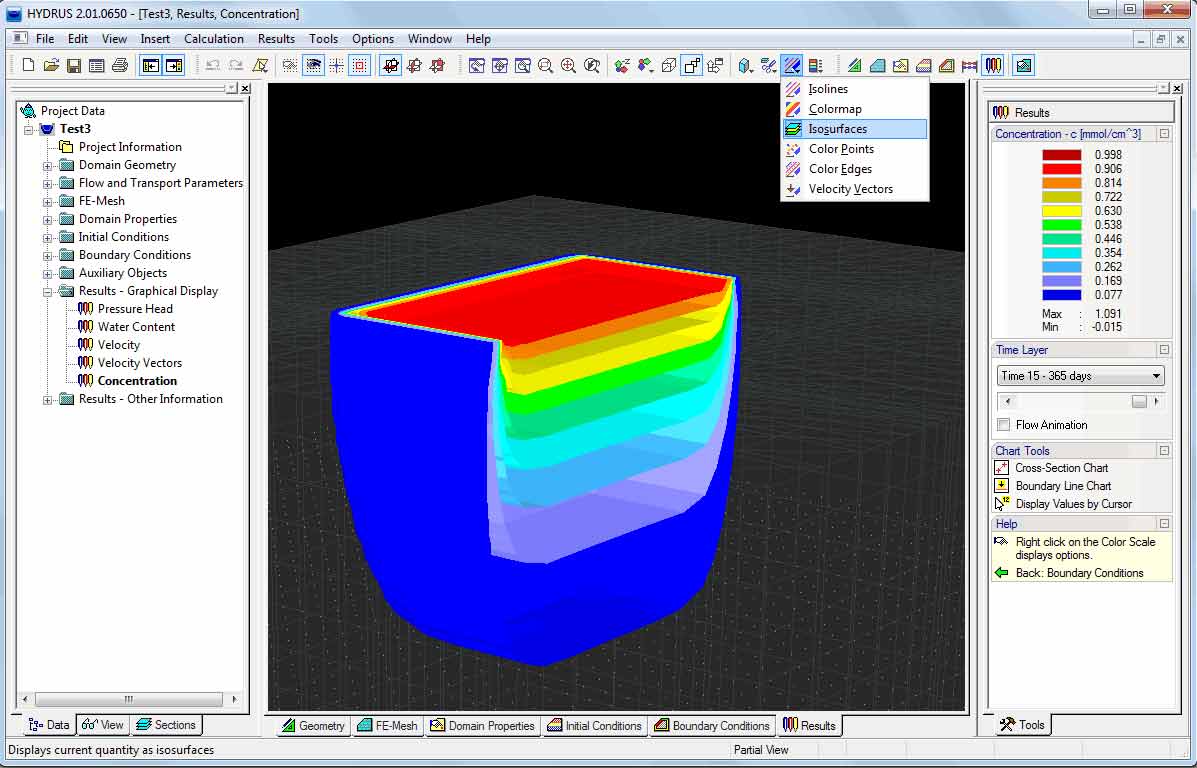
The output graph includes 2D contour lines (contour lines or color spectrum) of water content, flow rate, concentration and temperature in space or cross section view. The graphic output also includes speed vector graph, color edge, color point, graphic display and animation of continuous time steps, and selected boundary or internal section line graph. The user can zoom the area of interest, and the vertical scale of the cross section view can also be enlarged. The mesh can also represent triangles, edges, and points with boundaries and numbers. Observation points can be added anywhere in the grid. Views of the grid and/or spatial distribution results (pressure head, water content, velocity, concentration, and temperature) use high-resolution color or grayscale values. The interface also includes a rich online help menu.
Domain and finite element mesh region
To simplify the work of complex migration geometry, these graphics can be divided into simple parts called Sections. Only these simple parts can be displayed in the view window, while the rest are hidden. There are two types of Sections: geometric object based and finite element mesh based. Multiple sections can be displayed at the same time. Use various commands to cut off and hide unwanted parts of the migration area.
PC-Progress HYDRUS 2D/3D Pro 2.04.0580
HYDRUS is a Microsoft Windows based modeling environment for the analysis of water flow and solute transport in variably saturated porous media. The software package includes computational finite element models for simulating the two- and three-dimensionalmovement of water, heat, and multiple solutes in variably saturated media. The model includes a parameter optimization algorithm for inverse estimation of a variety of soil hydraulic and/or solute transport parameters. The model is supported by an interactive graphics-based interface for data-preprocessing, generation of structured and unstructured finite element mesh, and graphic presentation of the results.
HYDRUS is distributed in five different versions (Levels) so that users may acquire only that segment of the software that is most appropriate for their application. Users can select software limited to general two-dimensional applications (the 2D-Standard Level, which corresponds with former Hydrus-2D with MeshGen-2D) or for both two- and three-dimensional applications (i.e., 3D-Standard or 3D-Professional). Users can also opt for relatively simple (two-dimensional rectangular geometries – 2D-Lite [which corresponds with former Hydrus-2D without MeshGen-2D] or three-dimensional hexahedral geometries – 3D-Lite) or more complex geometries (i.e., 2D-Standard for general two-dimensional geometries, 3D-Standard for problems that can be defined using the general two-dimensional base and a layered third dimension, or 3D-Professional for applications with general three-dimensional geometries). Users may upgrade to higher Levels from lower Levels, as well as from lower versions (e.g., version 1.x) to higher versions (e.g., version 2 (and higher – in the future)).
HYDRUS 2D/3D for Windows
HYDRUS is a software package for simulating water, heat, and solute movement in two- and three-dimensional variably saturated media. The software package consists of a computational computer program and an interactive graphics-based user interface. A brief description of HYDRUS is given in the Introduction and Program Description. More detailed information is given in the User and Technical Manuals.
New version HYDRUS 2.05 has been released with the Slope Cube add-on module.
Please notice: Almost 50% of the World’s top 100 universities 2014 use HYDRUS for research or teaching purposes.
Reasons for using HYDRUS models:
Developed by leading (award winning) scientists in the field of vadose zone hydrology (Rien van Genuchten and Jirka Simunek). Always at the cutting edge of the most recent developments in vadose zone hydrology.
Considered to be a standard tool in both research and industrial applications. Also see the recently released HYDRUS book.
Used by thousands of users around the world (over five thousand of downloads in 2010 alone, and many more before and since then), including leading research institutions, regulatory agencies, and consulting companies.
Hundreds of successful applications (many reported in peer-reviewed journal articles – 1D, 2D, and 3D). Many successful examples of HYDRUS verifications and validations.
Hundreds of resolved problems in the HYDRUS public library of projects (1D, 2D, and 3D).
Easy to use and learn how to use (see the many free 1D and 2D, and 3D tutorials, and short courses organized around the world).
Hundreds of registered users in HYDRUS discussion forums allowing you to share your experience and learn from others.
Linked to other widely used programs in their respective fields of applications (MODFLOW, PHREEQC, Wetland Module, and Rosetta).
And many other reasons …
Hydrus-1D
Hydrus-1D is a public domain Windows-based modeling environment for analysis of water flow and solute transport in variably saturated porous media. The software package includes the one-dimensional finite element model HYDRUS for simulating the movement of water, heat, and multiple solutes in variably saturated media. The model is supported by an interactive graphics-based interface for data-preprocessing, discretization of the soil profile, and graphic presentation of the results.
Hydrus-2D
Hydrus-2D & Meshgen-2D, Last Version 2.1, May 2004
Hydrus-2D is not distributed any longer and was fully replaced in 2007 with HYDRUS 2D/3D.
Hydrus-2D is a Microsoft Windows based modeling environment for analysis of water flow and solute transport in variably saturated porous media. The software package includes the two-dimensional finite element model HYDRUS2 for simulating the movement of water, heat, and multiple solutes in variably saturated media. The model includes a parameter optimization algorithm for inverse estimation of a variety of soil hydraulic and/or solute transport parameters. The model is supported by an interactive graphics-based interface for data-preprocessing, generation of a structured mesh, and graphic presentation of the results. Optionally, the modeling environment includes a mesh generator for unstructured finite element grids, Meshgen-2D.
Home Page: https://www.pc-progress.com
Download address
Flow and solute transport simulation software PC Progress HYDRAS 2D/3D Pro 2.04.0580
Baidu online disk: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1jKd5qp4
Activation guide:
Build date: 20/05/2017
Program name: PC-Progress HYDRUS 2D/3D Pro v2.04.0580
Protection type: SoftwareKey Protection PLUS
Cracker’s names: raduga_fb/LAVteam
Instructions: Unrar.
Install the app. Do not install HASP drivers.
Start the app as admin (only once for the
activation), choose option Help -> Hydrus
License and Authorization and press
Activate by Email button.
Fill the form (Step 1):
License Number = 1907
Customer – any
WP Description – any
Expired Date < 1 year
HYDRUS level – any
and press generate Request Code button.
Copy Request Codes 1 and 2 (Step 2) to the
applied keygen.
Copy generated Activation Code back to the
Activation window (Step 3).





















![Wancai Animation Master | 0 Basic Animation Video [Software Recommendation] - Wood of Falling Dust](https://img.luochenzhimu.com/public/2024/05/2024051509.png)


![Official Windows 11 Release [Official MVS (MSDN)] [Windows 11 NI-23H2] February 2024 Image Update - Wood of Dust](https://img.luochenzhimu.com/public/2021/10/2021100515.jpg)




















































