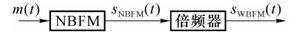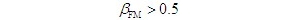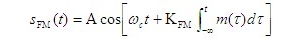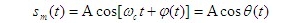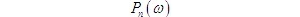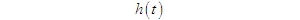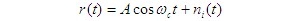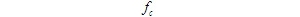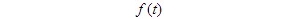Modern communication technology
- Anti noise performance of FM signal
-
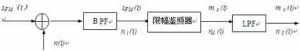
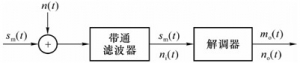
The analysis model is shown in Figure 1: Figure 1 Frequency discriminator demodulation anti noise performance model 1. Input signal to noise ratio received modulated signal is demodulator input signal power demodulator input noise is the same as linear modulation system demodulation, it is narrowband noise, and its power is. All
-
2015-3-25 09:17
- FM Signal Generation and Demodulation
-
The generation of FM signal usually includes direct FM method and indirect FM method. 1. Broadband FM signal generation 1) Direct FM method uses the modulation signal to directly change the reactance element parameters that determine the oscillator carrier frequency, so that the instantaneous frequency of the oscillator output signal changes linearly with the modulation signal. With
-
2015-3-25 09:04
- Broadband FM
-
Concept: 1. Single tone modulated WBFM signal time expression Set the modulated signal as single frequency cosine signal In order to further expand the above formula, it is necessary to use the property of Bessel function. Fig. 4.5.5 The curve of Bessel function of the first kind with the change of order 4.5.5 The curve of Bessel function of the first kind
-
2015-3-25 09:03
- Narrowband frequency modulation
-
The time-domain expression of FM signal is designed as a transcendental function, which brings difficulties to the frequency spectrum analysis of FM signal. Therefore, FM signal is studied in two cases. Generally, we define the FM signal at that time as narrowband FM signal. With the help of mathematical formulas, you can
-
2015-3-25 09:02
- Basic concept of angle modulation
-
Angle modulation can be divided into frequency modulation (FM) and phase modulation (PM). That is, the modulation mode in which the amplitude of the carrier remains unchanged while the frequency or phase of the carrier changes with the baseband signal. The general expression of angle modulation signal is called instantaneous phase, which is called instantaneous phase offset; Is the instantaneous angle
-
2015-3-25 09:01
- Anti noise performance of amplitude modulation system
-
The problem studied in this paper is the anti noise performance of various linear modulation systems when there is additive white Gaussian noise in the channel. Considering that the additive noise in the channel only affects the reception of the modulated signal, the anti noise performance of the modulation system can be measured by the anti noise performance of the demodulator. The analysis model is shown in Figure 1
-
2015-3-25 09:00
- Single sideband (SSB) and vestigial sideband (VSB) modulation
-
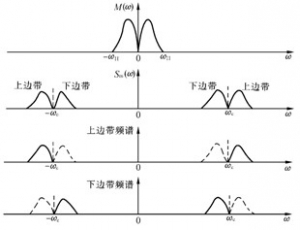
1、 Single sideband amplitude modulation 1. Definition of single sideband modulation: the modulation method that transmits only one sideband is called single sideband modulation (SSB). The spectrum of SSB modulated signal is visible. SSB modulation has two modes: only transmit the upper sideband or only transmit the lower sideband. By single sideband
-
2015-3-25 08:58
- AM and DSB modulation
-
Amplitude modulation: the amplitude of the sine wave changes linearly with the modulation signal. The general model of the amplitude modulation signal is the general model of the amplitude modulator in Figure 1. 4.2.1 Time domain analysis of the amplitude modulation wave (time expression and time waveform) Definition: the amplitude of the carrier changes linearly with the modulation signal. Marked by
-
2015-3-25 08:57
- Gaussian white noise and band limited white noise
-
When analyzing the anti noise performance of communication systems, Gaussian white noise is usually taken as the noise model of communication systems. At this time, the fluctuation noise (including thermal noise and shot noise) in the communication system can be approximated as white noise and obey the Gaussian distribution. 1、 If the power spectrum of Gaussian white noise is dense
-
2015-3-24 09:00
- Stochastic process through system analysis
-
1、 A stationary random process passes through a linear system. If the impulse response of the linear system is, and the input random process is, then the output random process is equal to the convolution of and, that is, 1. The mathematical expectation of the output random process assumes that the input stationary random process is, and its mean value is, after transmission by the linear system, the output random process is
-
2015-3-24 09:00
- Cosine wave plus narrowband stationary Gaussian process
-
In the communication system, the noise in the channel can be considered as Gaussian white noise. In order to reduce the impact of noise and improve the reliability of the system, a band-pass filter is usually set at the front end of the demodulator. After passing the band-pass filter, the Gaussian white noise in the channel becomes narrow-band Gaussian noise. For this narrow-band noise
-
2015-3-24 08:58
- narrowband random process
-
All communication systems have transmitters and receivers. In order to improve the reliability of the system, a band-pass filter is usually connected to the input terminal of the receiver. The noise in the channel constitutes a random process. After passing the band-pass filter, it becomes a narrow-band random process. Therefore, the law of discussing the narrow-band random process is
-
2015-3-24 08:58
- Gaussian random process
-
Gaussian random process, also known as normal random process, is a kind of ubiquitous and very important random process in communication systems. In general, the noise in the communication channel can be regarded as a Gaussian process. 1、 Gaussian random variable and Gaussian random process 1. Define any
-
2015-3-24 08:56
- Stationary stochastic process
-
Stationary stochastic process is a special and widely used stochastic process. 1、 Definition of stationary stochastic process 1. The dimensional distribution function or the dimensional probability density function of the narrow stationary stochastic process is independent of the starting point of time, that is, for any sum, the dimensional probability density function of the stochastic process satisfies
-
2015-3-24 08:55
- Partial Description of Stochastic Processes -- Numerical Characteristics
-
Although the statistical characteristics of random processes can be perfectly described by using the dimensional distribution function or the dimensional probability density function of random processes. But in practical work, it is sometimes difficult or unnecessary to solve the dimensional distribution function or the dimensional probability density function, and the digital characteristics of random processes can describe the important characteristics of random processes, and
-
2015-3-24 08:53
- General Concept of Stochastic Process
-
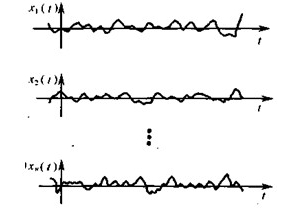
1、 The basic concept of random process The definition of random process When the process of change of things cannot be described by one or several time deterministic functions, the process is called random process. Figure 1 The basic characteristics of the process of recording the noise output of a communicator are as follows: First, in the observation area
-
2015-3-24 08:52
- Hilbert transform and analytic signal
-
Definition: Time expression obtained by phase-shifting all frequency components in the signal. Definition of Hilbert transform Hilbert transform: from the above formula, we can see that the positive transformation of Hilbert transform can be regarded as a linear system, and its impulse response should be, as shown in Figure 1. Fig. 1 Hilbert transform forward
-
2015-3-24 08:51
- Confirm that the signal passes through the linear system
-
1. Time domain description of the output signal Figure 1 Signal passes through a linear system 2. Frequency domain description of the output signal describes the transmission function of the system. 3. Energy spectral density or power spectral density of output signal If the input signal is an energy signal, the energy spectral density of output signal is if
-
2015-3-24 08:51