The Formation Mechanism of IT Industry Monopoly and the New Characteristics of Competition
5.1.1 Formation mechanism
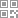
1. The formation of regulatory monopoly under the dual economies of scale of the supply side and the demand side
As shown in the figure, under the dual role of supply side economies of scale and demand side economies of scale, The optimal point of the economic scale and efficiency of enterprises in the IT industry may tend to be borderless, so the market will show the characteristics of "leaning to one side" and "rising to the top". The result of market equilibrium will concentrate on a certain product or technology, and the result of concentration is that the market structure will constantly change to a monopoly or oligopoly market structure.
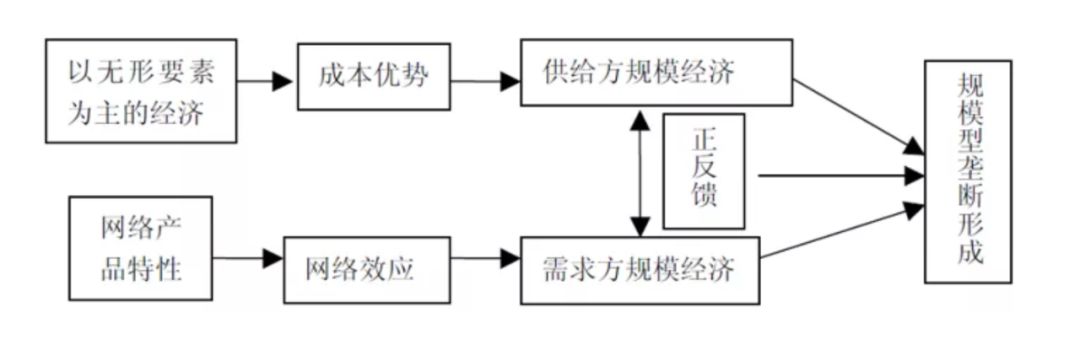
2. Formation of technological monopoly under property rights protection and standard competition
In the information economy era, technological innovation and the mastery of standards have become one of the key factors for enterprises to gain a monopoly position in the market. The systematic and complementary nature of network products objectively requires technology to achieve a high degree of standardization, while the high degree of standardization of technology forces the market to tolerate only one or a few technologies at the end, The result of market competition in which a large number of technological innovation subjects and a limited number of technical standards can survive makes the competition for technical standards in the network industry extremely fierce. The winner in the standard competition can not only occupy the market monopoly position of "all winners" or "the majority winners", but also obtain huge economic benefits. Those who get the standards win the world. Those who master the technical standards will have the right to formulate the rules of the game, and will be able to gain greater technological control and market power, so as to control the future development direction of technology and gain industrial leadership.
In the traditional economy, standards are the public rights imposed by public institutions such as standardization institutions. When collecting standards, standard setting institutions generally try to avoid including intellectual property or patent rights with private attributes into standards. Standards with public rights are not exclusive to one enterprise, but must be followed by all similar enterprises. Since such standards do not limit the specific technologies adopted by enterprises to meet the standards, the most efficient and easy to implement technology will win the competition. Therefore, the formulation and implementation of such technical standards promote the technological competition between enterprises. In the information economy, due to the strong awareness of property rights protection of enterprises, as long as there is innovation, they will consider applying for patents. Few technical standards can bypass intellectual property rights or technology patents. The involvement of private property rights in technical standards means that standard holders have exclusive market power. If other enterprises want to use this standard, they must pay relevant intellectual property rights fees or technology patent fees to the standard holders. The negative impact of technical standards on competition is increasingly exposed. In market competition, standard holders can easily gain market advantages by virtue of technical standards.
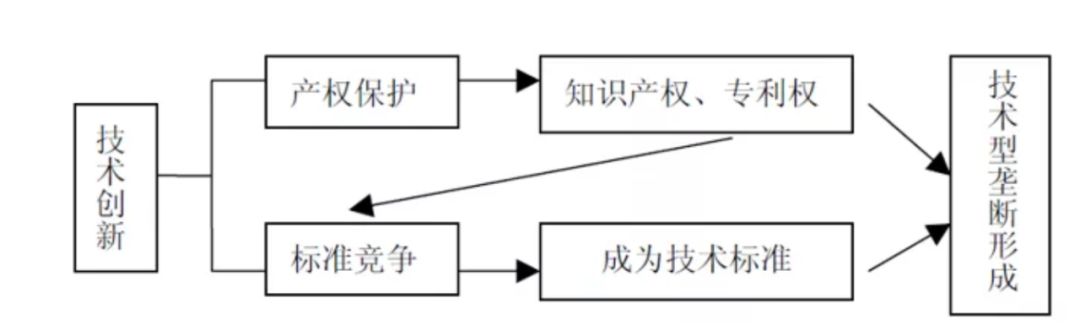
3. The formation of endogenous monopoly based on its own advantages and strong learning effect
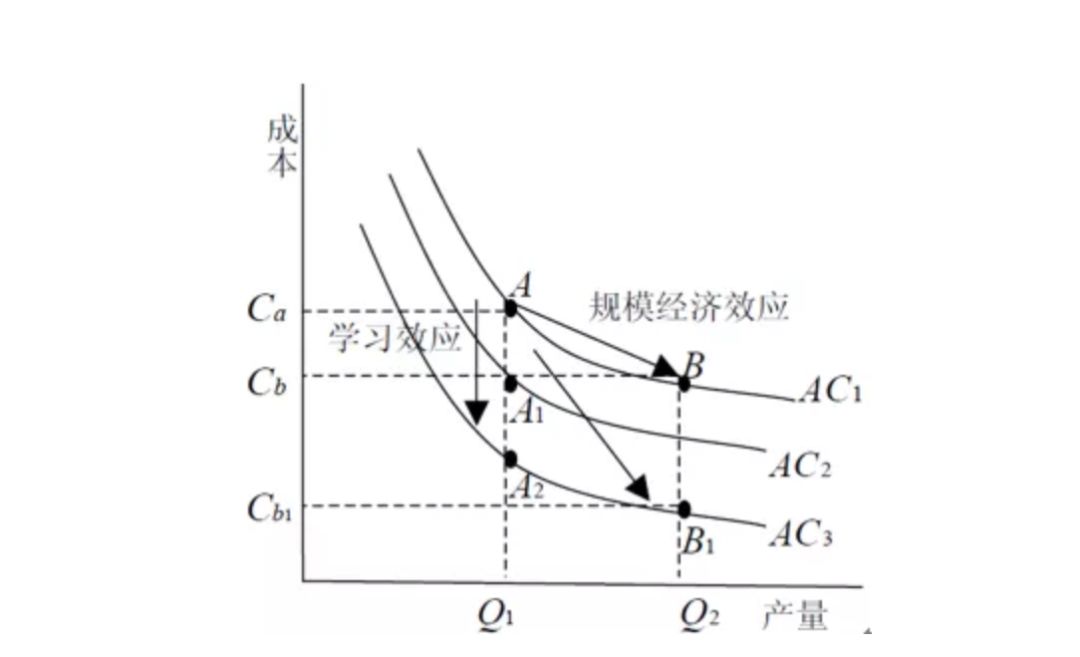
Unlike the traditional monopoly enterprises, which become the "Big Mac" of the industry by external forces such as administrative support and annexation of competitors, the monopoly of network enterprises (such as Microsoft) in the network economy society is basically based on the "self growth model" and formed in the market competition, so it is an endogenous monopoly. The monopoly of enterprises is based on their own product advantages, efficient operation and management, cumulative learning effect and providing quality services to consumers. It is the result of the survival of the fittest in the market competition following the "Darwinian survival law".
5.1.2 New features of IT industry competition
Market Share has become the key to determine the outcome of the competition.
"Winners almost take all" is an important driving force for competition.
Standard competition is the main form of competition.
Locking users is an important strategy for competition.
Alliance and compatibility are important ways to gain competitive advantage.
Competitive behavior and strategy selection
Due to the differences between the economic environment and laws of IT industry operation and the factors that affect the operation results of the network industry and traditional industries, some strategic behaviors prevalent in traditional industries, such as collusion and restrictive pricing, lack suitable soil for survival in the network industry, or at least are not as effective as in traditional industries. According to the characteristics and operation rules of the information economy, this paper discusses the strategic behavior suitable for the characteristics of the IT industry.
5.2.1 Competition and Mainstream Strategy for Market Share
The core and key of the product mainstreaming strategy is to make the product become the mainstream product, and whether it can become the mainstream product depends on the size of the product market share, so trying to expand the market share becomes the direct goal of the product mainstreaming strategy. In the expansion process of product market share, the critical point is very important. Once the number of users of the product exceeds the critical point, the market share can expand on the original basis without external force. The network effect of the existing user base can provide enough utility to encourage more users to participate, This positive feedback mechanism will continue to work until the maximum balanced user share is obtained. The critical point can be said to be the watershed between the success and failure of the product mainstreaming strategy. The positive feedback mechanism's virtuous circle and vicious circle, as well as the "winner takes all" and "loser takes all" phenomena illustrate the cruelty of market competition in the network economy. The mainstreaming of one enterprise's products is often at the expense of the mainstreaming of another enterprise's products, in other words, The process of product mainstreaming of one enterprise is just the process of product non mainstreaming of other enterprises. Therefore, the non pricing strategy for the mainstream of network products can be divided into two major aspects, namely, the strategy to promote their market share to reach the critical point as soon as possible and the strategy to restrain and delay competitors' market share to reach the critical point.
1. Strategies to accelerate the expansion of product market share and make it reach the critical point as soon as possible
a. Take the lead in launching products and become the market navigator.
b. Selectively open, make full use of the open network effect to expand the user scale.
c. Establish consumption leaders and overcome the inert obstacles in consumption choices.
d. Improve the technical content of products and reduce the user scale required for critical points.
2. Strategies to restrain and delay the market share of competitors' products reaching the critical point
5.2.2 Stability and locking strategy of user base
Although the expansion of market share is the direct target and measurement index of product mainstreaming, the position of product mainstreaming may not be sustainable with only such quantitative index expansion, and the duration of the position of product mainstreaming depends on whether the expanded market share is stable. Because the market competition is dynamic, it is normal for product suppliers to have a temporary reduction in market share, but it cannot be reduced below the critical user base. The user base at the critical point is the low line of the positive feedback mechanism virtuous circle. The truly successful mainstream network enterprises must be able to maintain the user base of their products in the subsequent competition to ensure that this part of the expanded market share is highly stable. Locking is an effective strategy to maintain the stability of the user base of network enterprises.
In real economic life, it is not only customers who have a headache about locking, but also post market entrants who hate locking. Locking increases the difficulty for their products or technologies to enter the market. They always try to break the lock. In the era of network economy, market share is crucial to the survival and development of enterprises. In order to stabilize market share or avoid the existing market share being seized by other enterprises, network enterprises have taken locking strategies.
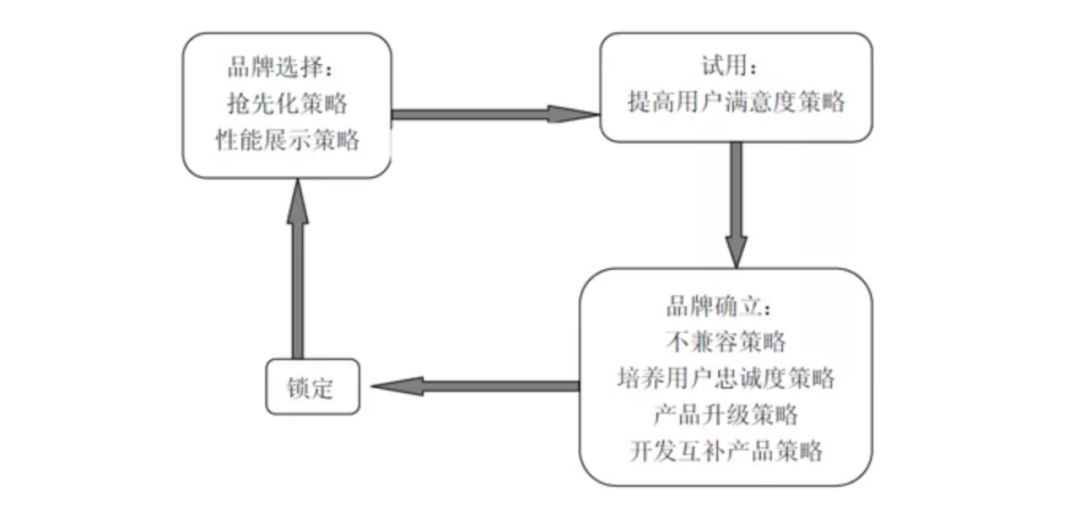
5.2.3 Standardization and standard competition strategy
"Third rate enterprises sell coolies, second rate enterprises sell products, first-class enterprises sell patents, and super first-class enterprises sell standards".
Although standards are not new in the era of network economy, their importance to market competition is most prominent in this era. Standards are the core factor of IT enterprise competition. Winning standards means winning the market, which is the so-called "standards winner wins the world".
1. Factors affecting the success or failure of standard competition
There are winners and losers in the market competition. If IT enterprises want to win in the standard competition, they must support
There are some key assets. These key assets mainly include six types: control of user installation base, intellectual property rights, innovation ability, production capacity, power of complementary products, and brand and reputation. These six key assets play an important role in the success of enterprises in the standard competition.
2. Standard competition strategy
Reasonable strategies improve the possibility of enterprises winning in standard competition. In order to improve the probability of winning in the standard competition, enterprises must plan and design the strategy of standard competition from a strategic perspective, including:
a. Set appropriate competition goals
b. Choose the right time to enter
c. Internal resources needed to foster standard competition
d. Reasonable organization
5.2.4 Product differentiation competition and compatibility strategy
Product differentiation and compatibility are relative. Differential performance provides consumers with diversified choices to meet their different preferences, but it also brings incompatibility problems, which inhibits the network effect of products or technologies in the network industry with network externalities; Although compatibility can expand the network scale of products or technologies, it can also reduce product diversification and product differentiation. Therefore, network enterprises must make decisions on the positioning of products or technologies between differences and compatibility. An important factor affecting the decision of manufacturers is consumer preference. If there is no difference or no obvious difference in consumers' preference for a product or technology, the value of the product or technology is mainly reflected in the network scale. The larger the network scale, the easier it is for consumers to choose; On the contrary, if consumers' preference for a product or technology is large enough, even if the network size of the product or technology is small, its value in consumers' minds will not be affected. The satisfaction of consumers' heterogeneous preference can compensate for the loss caused by the decline of network effect.
Compatibility has always been an important issue in the study of industrial organization theory. In the network economy, compatibility is no longer a purely technical issue for enterprises, but a competitive strategy issue. On the one hand, for some system network products composed of components, if there is no mutual compatibility between components, the system will not work normally; On the other hand, product compatibility is related to the construction and expansion of product user scale. For new entrants, if they can achieve compatibility with incumbent manufacturers, they can quickly establish the user scale of new products; For incumbent manufacturers, achieving compatibility with new entrants or other incumbent manufacturers may further expand their user scale, or gradually reduce their user scale due to the involvement of other manufacturers. The former is a problem of compatible technology, and the latter is a problem involving enterprise competitive strategy.
Compatibility can be achieved in two ways: standardization; The second is the add-on adapter. Standardization refers to the provision of uniform technical standards for relevant parties in a certain field as required. To achieve compatibility in a standardized way is to design the unified technical standards required for the integration of related products or technologies in advance (such as unified provisions on computer interfaces or interfaces), and urge all interested parties to comply with them through agreements, so that products or technologies can be interconnected and interoperable. The mode of additional adapter is applicable to products or technologies with different technical standards. It is to attach a conversion device between products or technologies that cannot be merged to enable them to be interconnected and interoperable to a certain extent.
Among the two ways to achieve compatibility, standardization is relatively advantageous. Compatibility realized by standardization is a kind of prior compatibility. Unified technical standards have been included in the process of product production or technical design, making the compatibility performance between products or technologies better and more stable, and achieving full compatibility. Therefore, in economic reality, most compatibility is achieved through standardization, However, compatibility realized in a standardized way may also cost too much due to prior design, coordination and agreement
Embrace, expand and destroy
Embrace, expand and destroy (English: Embrace, Extend, and extend) is a phrase found by the U.S. Department of Justice inside Microsoft, which expresses a development strategy used by Microsoft, namely: first, accept widely used technical standards, push products to the market, then add their own patent extensions to products, and finally use these non-standard patent extensions to put competitors at a disadvantage.
In 1993, Marc Andreessen, 22, invented the world's first web browser Mosaic, and launched Netscape the following year. Before that, surfing the Internet was a technical job, and Netscape's role was to take over this complex process and provide users with a graphical browsing interface. This means that the threshold for browsing information on the Internet has been greatly lowered, as long as you have a computer and are willing to pay a sum of money for Netscape browser.
The era of web browser created by Mosaic and Netscape soon ushered in the technology giant: Microsoft. In 1995, Microsoft released Internet Explorer (IE), which was widely criticized in the future. Several earlier versions of IE still lag behind Netscape in technology, but Microsoft has left behind: IE is bundled with Windows 95 operating system and provided for free. Around 1998, IE began to surpass Netscape in market share.
In 1998, Netscape announced two decisions. The first decision did not surprise the industry: the Netscape browser Navigator will be provided for free in the future; The second decision was beyond many people's expectations: Netscape will disclose the code of the next-generation Netscape Communicator suite.
Netscape's disadvantage is that its main product is the browser, and it cannot rely on the powerful operating system like Microsoft to support browser projects. Therefore, free is not only a last resort, but also full of risks. Open source shows a gesture: since it is free, it should be completely free.
On the second day of the announcement of open source, Netscape registered the website mozilla.org. This open source project named "Mozilla" gave birth to the famous Firefox browser. In July of that year, Netscape announced that it would cooperate with the open source operating system Linux to provide open source software for future Linux systems. From many perspectives, Firefox is quite ahead of Internet Explorer. Even so, Internet Explorer still has more users, regardless of its advanced features or technology.
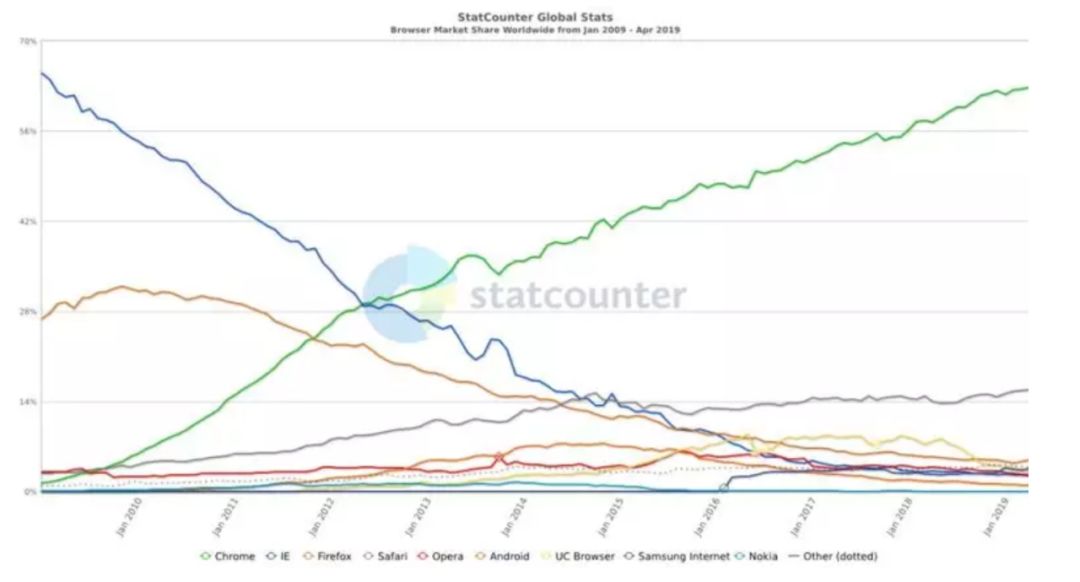
Everything changed when Google released Chrome. In the first few months of Chrome's release (September 2008), IE accounted for more than 60%. In StatCounter's January 2019 report, Chrome accounted for more than 70% of the total.
Chrome is considered to be a model of "strategic openness". Chrome is open source. It is based on Chromium, and anyone can download this kernel, or even participate in contributing code. Some people have developed their own browsers based on Chromium: Brave is a newcomer, Opera is an old brand, and even Microsoft's new Edge is based on Chromium.
At the same time, Google has done a lot of work in the standardization of Internet components, the most prominent of which is the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). It is conceivable that an entity like Google, which dominates the web browser market, is deliberately promoting the integration and standardization of the Internet mechanism to consolidate its dominant position in technology.
Google has opened many large-scale products, and has benefited a lot from this "openness" initiative: on the one hand, it has received contributions from the broad developer community, and on the other hand, its products have been widely adopted. Android is a good example, but Chrome is also a good example. Other examples include Kubernetes and TensorFlow.
Carlotta Perez Technological Revolution and Financial Capital: Dynamics of Bubbles and the Golden Age, 2007
Christopher Freeman From Industrial Revolution to Information Revolution, 2007
Wang Guangfeng Competition between open source software and proprietary software -- Research based on system software market, 2008
Guo Yubiao A New Property Right System and Production Mode in the Knowledge Economy -- Research Based on the Phenomenon of Open Source Software, 2004
Wang Ling, Dong Zhenwei, Wu Yongqing Structural analysis of open source software business model, 2018
Yan Xianjun Information monopoly: new changes of contemporary capitalism in the perspective of information technology revolution, 2010
Information and Communication Institute White Paper on China's Information Economy Development, 2016
Tao Aiping Research on the Structure, Behavior and Performance of the Network Industry, 2009
http://ocselected.org/posts/paper_or_book_reading/thinking_of_open_source_innovation_economic/
https://msd.misuland.com/pd/3691885065085650670
https://www.cbinsights.com/research/report/future-open-source/
https://www.gnu.org/philosophy/categories.html
https://www.gnu.org/philosophy/free-software-for-freedom.zh-cn.html
https://www.lieyunwang.com/archives/459467
https://www.3wcoffee.com/qfnews/detail?id=2365
http://mini.eastday.com/a/190213150603957-4.html
http://www.360doc.com/content/19/1111/21/16295112_872512062.shtml
https://m.huxiu.com/article/305943.html
http://www.wowotech.net/tech_discuss/Unix%E7%9A%84%E5%8E%86%E5%8F%B2.html
https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/UNIX
https://coolshell.cn/articles/2322.html
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/46702640
https://linux.cn/article-6783-1.html
https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/BSD
http://kuanghy.github.io/2015/06/07/os-history
http://finance.eastmoney.com/a/201912121321723219.html
https://riehle.org/computer-science/research/2007/computer-2007-article.html
https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E6%8B%A5%E6%8A%B1%E3%80%81%E6%89%A9%E5%B1%95%E5%86%8D%E6%B6%88%E7%81%AD
https://xueqiu.com/5215025851/118877584
http://www.qdaily.com/articles/60527.html
https://linux.cn/article-10714-1.html
*The pictures in this article are from the network. If there is infringement, please contact to delete!
Introduction to Kaiyuan News Agency
The Open Source Society is a manufacturer neutral, volunteer and non-profit open source alliance organized by enterprises, communities and individuals at home and abroad who support open source in accordance with the principle of "contribution, consensus and co governance", aiming to jointly create a healthy and sustainable open source ecosystem and promote the Chinese open source community to become an active participant and contributor of global open source software. We focus on open source governance, international integration, community development and open source projects.
Related reading | Related Reading

Analysis on the evolution of open source software from the perspective of technology economy paradigm (4)

Analysis on the evolution of open source software from the perspective of technology economy paradigm (3)

Analysis on the evolution of open source software from the perspective of technology economy paradigm (II)

Analysis on the evolution of open source software from the perspective of technology economy paradigm (I)