What are the differences between SIL1, SIL2 and SIL3
Time: 2022-02-20 11:18:02 Source: Yonglong Valve Reading: zero second
What are the differences between SIL1, SIL2 and SIL3
What is the difference between SIL1, SIL2 and SIL3 in the definition of instrument safety level? Since SIS involves the safety of personnel, equipment and environment, all countries have formulated relevant standards and specifications, so that the design, manufacture and use of SIS can be followed. Yonglong Valve is explained as follows:
ESD (Emergency Shutdown Device): emergency shutdown system, mostly used in petroleum and chemical systems, is a control unit independent of DCS system, which can start and switch equipment and environment in case of dangerous process conditions. Most of the configuration equipment is high-end PLC, most of which process DI/DO points, and now most of them communicate with DCS.
SIS (SIS, safety instrumented system): safety instrumented system, mainly used for high-speed running equipment such as steam turbines and compressors, to detect the speed, vibration, displacement, temperature, etc. of bearings, and to protect the equipment. The original design is mostly module combination, which is equivalent to the combination with intelligent instruments. SIS is a safety instrument system, ESD is an emergency shutdown system, and ESD is a part of SIS. SIS includes three parts: field instrument, logic resolver and actuator. These three parts should be designed safely. The conventional ESD system is only the logic resolver of SIS. Of course, it should also be designed safely.
A random example may not be appropriate, but it can help to understand these concepts. Siemens PCS7 system. It includes S7-400H hardware, WinCC monitoring software and Simaticnet communication software. Step7 Programming software. PDM and other intelligent instrument tools.
PCS7 is a combination of a series of software and hardware. It is a system concept.
SIS is basically the same.
Essentially, SIS hardware system not only includes SIS controller and IO (such as Triconex, HIMA, Siemens 400FH).
It shall also include all other input components that interface with the controller, such as sensors, transmitters and detection devices that have obtained TUV SIL certification;
It should also include all output components, such as actuators certified by TUV SIL (hydraulic safety actuator, pneumatic safety actuator, electric safety actuator),
There should also be certified field equipment. On the site with strict requirements, the valve body must also have a TUV certificate.
For example, the safety valves of nuclear power plants should not only be qualified in the quality inspection of boilers and pressure vessels, but also have a nuclear inspection certificate, as well as a TUV safety certificate, clearly indicating the SIL level.
Now, let's understand that these concepts,, and security controllers (the most scientific name at present) are just one part of the SIS system hardware.
Manufacturers of safety controllers include Triconex, HIMA, Siemens, Moore, ICS, ABB, EMerson, etc.
These safety controllers are called ESD when they are used for emergency shutdown.
Fire detection and gas alarm for oil and gas fields are called F&GS
For combustion control in dangerous places, it is called BMS.
ESD, F&GS and BMS do not refer to Triconex, HIMA or their controllers. Instead, the security controllers of these manufacturers are used in these different occasions and have different purposes, so they have different names.
Next time, someone asks you why Triconex is called ESD, PSD, F&GS and BMS. Also called SIS... You should understand its meaning. These are safety controllers, or safety control systems, or safety systems (PES), safety electronic devices, as the IEC specification once called them.
When it is used in the case of ESD, it is ESD, and when it is used in the case of F&GS, it is F&GS
SIS is a complete and systematic concept. From its naming, we can see that it is a complete concept and a system that pays more attention to integrity.
The whole safety is based on the whole safety mechanism, including safety controllers (such as ESD, F&GS, BMS,,,), safety instruments, safety actuators,
Safe software (function block library, chain specification), and even "safe communication function" (which is rarely called at present).
The integrity concept of SIS shall also include specifications throughout the whole life cycle of the safety control system, such as initial design, mid-term construction and commissioning; Final commissioning, evaluation and verification.
Subsequent maintenance. Dismantling before the safety life cycle reaches the limit...
In short, the concept of SIS is very complete and huge The first one is always the design institute, and then the design institute fools the owner...
Then many people who do SIS and adjust ESD have been doing it for several years, and the concept is also dizzy.
Why are SIS more mentioned in bidding these years?
Theoretically, only ESD, "may not" be a complete SIS control system. ESD is only one part of SIS and the most important part of physical hardware.
Therefore, many people believe that SIS is ESD... ESD is SIS.
With ESD, there are many surrounding supporting equipment. A SIS control system can be formed.
Users want a complete security control system, so in recent years, the bidding specifications are called SIS, hehe.
To be honest, it is true that the soup is not changed, but at least it shows that our users have made progress in the integrity of the security concept,
No matter how much progress you have made, or how much you have improved yourself, you have always made progress.
Similarly, (I once heard from the deputy sales manager of a well-known DCS that Siemens DCS, pcs7 is S7-400 PLC, S7-400 PLC is PCS7 DCS, hehe)
Many things are not simple equivalents!
ITCC。 Control of high-speed rotating equipment, such as steam turbine control, air compressor control, blast furnace blower control. Even turbine engine control, gas turbine control is another concept. For example, the controller of Triconex can do ITCC in addition to ESD and F&GS.
The system under SIS concepts such as ESD, F&GS is to be certified and must have TUV SIL level certificate. For ITCC, TUV certification is not necessary.
The same thing in the same family, used in different occasions, has different uses, so it has different names. In the same way, you have a lot of money. You can use the Triconex system as a PLC or a small DCS. At this time, you can also call triconex PLC or DCS.
CCC is for ITCC, not ESD; Yokogawa and Emerson's security systems are basically ESD, F&GS, not ITCC. Triconex is both ESD and ITCC.
SIS safety instrument system
ESD emergency shutdown is generally called ESD in petrochemical industry. It is called HIPPS on the high-pressure pipeline, FSSS on the boiler and ETS on the turbine.
ESD is a part of SIS, which is an important part SIS=ESD+intermediate wire+field instrument or actuator.
ESD is called SIS, which is not reasonable
At present, many projects require SIS system to reach SIL3. It is not enough just for ESD to reach SIL3, but also for field instruments to reach this level, and the entire control loop formed to reach SIL3
When ESD first came into China, it should have been done well by ICS, then by HONEYWELL, and then by triconex, which was represented by Kongson. After 2000, HIMA came in. Recently, it seems that triconex and HIMA have more market shares.
In addition, ITCC is the name proposed by Kongson. Since it conflicts with the contents in IEC61508 and 11, it is said that now the design institute has begun to change its name to CCS. With reference to the ETS+DEH mode of the power system, I personally think it is better to separate the control and protection of the compressor, and use ESD+speed regulation+anti kick
As far as the PCS (process control system) of the refinery is concerned, the integrated control system of the refinery is composed of DCS, ESD, CCS, MMS and CGTCS, and DCS is the core of control. ESD (Emergency Shutdown Device) ------ emergency shutdown system (including SOE), independent of DCS system, is SIS (safety instrumented system): safety instrumented system is mainly composed of emergency shutdown of pipeline and equipment to achieve protection in case of dangerous process conditions. Different from DCS in system structure and communication mode in design, 2-o-o-3 voting Triconex system and HART communication mode are used for Ethernet communication with DCS. To ensure the coordinated and safe operation of the whole plant, the ESD system also needs to communicate with CCS (compressor control system), MMS (machine monitoring system), CSTCS (gas turbine control system), and MCC (motor control center) to complete the safety protection requirements.
SIS is a safety instrumented system, and ESD is a part of SIS. SIS includes three parts: field instrument, ESD system and emergency on-off valve. HART+4 --- 20mA communication connection is adopted. SIL assessment is required for each ESD circuit. In order to achieve SIL2 or SIL3 safety level, two solenoid valves are used to control the emergency opening and closing valves, three differential pressure transmitters are used to measure the same level, and radar and ultrasonic instruments are used to measure the same level. Of course, SIL calculation verification is required to ensure that the system meets the requirements.
Definition and difference of instrument safety level, what is the difference between SIL1, SIL2 and SIL3?
Since SIS involves the safety of personnel, equipment and environment, all countries have formulated relevant standards and specifications, so that the design, manufacture and use of SIS have rules to follow. And there is an authoritative certification authority to confirm the safety level that the product can reach. These standards, specifications and certification bodies mainly include:
SHB-Z06-1999, the industrial standard formulated by China Petrochemical Group, is the Design Guide for Petrochemical Emergency Shutdown and Safety Interlocking System.
In 2006 and 2007, China's national standards GB/T20438 and GB/T21109, which are equivalent to IEC61508 and IEC61511, were issued successively, and China's functional safety standards began to regulate China's functional safety work.
The IEC 61508/61511 standard formulated by the International Electrotechnical Commission in 1997 clearly stipulates the hardware, software and application of the safety interlocking system composed of electromechanical equipment (relay), solid-state electronic equipment and programmable electronic equipment (PLC).
ISA-S84.01-1996 Application of Safety Instrumented System in Process Industry formulated by American Instrument Society.
AICHE (ccps) - 1993, Guidelines for Safety Automation of Chemical Processes, prepared by the American Chemical Engineering Society.
HSE PES-1987, Application of Programmable Electronic Systems in the Field of Safety, prepared by the British Health and Safety Executive Committee.
German national standards include safety system manufacturer's standard DIN V VDE 0801, process operation user's standard DIN V 19250 and DIN V 19251, combustion management system standard DIN VDE 0116, etc.
The German Technical Supervision Association (T ∨ V) is an independent and authoritative certification body. According to the German national standard (DIN), it divides the safety level reached by ESD into AK1~AK8, and AK8 has the highest safety level. AK4, AK5 and AK6 are SIS products applicable to petroleum and chemical industries that have obtained TUV certification
Different industrial processes (such as production scale, types of raw materials and products, complexity of processes and equipment, etc.) have different requirements for safety. The above international standards divide it into several safety integrity levels (SIL).
Safety integrity level (SIL) is a discrete level used to specify the safety integrity requirements assigned to the safety functions of E/E/PE safety related systems.
The safety integrity level can be divided into four levels, SIL4 is the level with higher safety integrity (the highest average probability), and SIL1 is the lower level; For example, the electric shut-off valve, pneumatic shut-off valve and emergency shut-off valve of Shanghai Yonglong Valve Factory have passed the SIL3 instrument safety level certification.
The higher the safety integrity level, the higher the probability that the required safety function should be performed;
According to the use mode of safety related systems, the frequency of requirements can be divided into low requirement operation mode (<=1 time/year) and high requirement or continuous operation mode (>1 time/year).
According to GB/T 20438 standard, the target failure probability and target risk reduction of safety integrity under different operation modes are shown in Table 1-1 and 1-2 below.
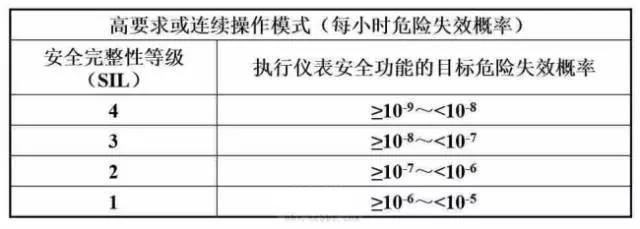
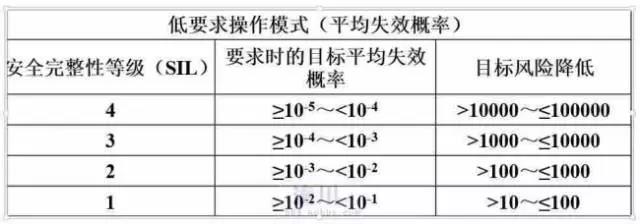
Using different operation mode structures, it is possible to use several systems with lower safety integrity level to meet the needs of a higher safety integrity level function (for example, using a SIL2 and a SIL1 system to meet the needs of a SIL3 function).
Different technological processes (production scale, types of raw materials and products, complexity of processes and equipment, etc.) have different requirements for safety. For a specific process, whether SIS needs to be configured and what level of SIS needs to be configured should be based on risk assessment of this specific process, hazard and operability analysis (HAZOP), and identification of safety instrumented function (SIF) corresponding to this analysis (finding a safety instrumented interlock loop), Then, according to the frequency of risk occurrence and its serious consequences, find a SIL value corresponding to this SIF, and after determining the integrity level (SIL) of a safety instrumented function, configure the corresponding SIS. It can be seen from Table 1-3 that if the required SIF of a process is SIL 2 after evaluation, then SIS with AK4 can be configured, and its response failure rate (PFD) is between one percent and one thousandth.
It should be noted that SIS with different safety levels can only ensure that the response failure rate (PFD) is within a certain range. The higher the safety level is, the smaller the PFD is, that is, the smaller the possibility of accidents, but it cannot change the consequences of accidents. Therefore, the assessment of process safety integrity level is a very important work. However, there are no standards and specifications on how to assess the safety integrity level in China. Some evaluation methods are provided in international and foreign standards. The risk matrix (RISK MATRIX) assessment method described below can be used for reference.
In this method, the frequency (possibility) and hazard degree (severity) of process accidents are taken as the indicators of risk assessment, and the frequency and hazard degree are artificially quantified into several levels, making a matrix table (see Table 3). So as to determine the safety integrity level of the process.
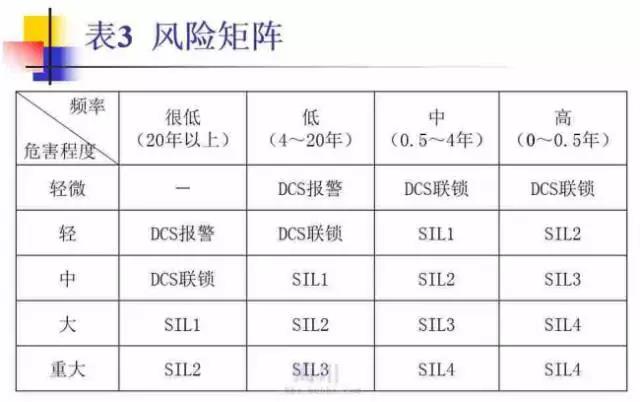
SIL level cannot be modified by configuration, which is based on calculation. The SIL level of the system indicates that the system can be used in a certain SIL level situation, of course, the system reaching SIL3 level can also be used in SIL2 situation. And according to IEC61508, SIS (Safety Instrumented System) not only requires the control system to have SIL level, but also requires the on-site instrument valves to have SIL level. It is not only that each component (monitoring instrument, control system, actuator, etc.) constituting a control loop has SIL level, but also needs to calculate the PFD of the whole control loop. If the calculated PFD is within the scope of SIL 2, Then the control circuit reaches SIL level. Whether a control loop is required to be SIL2 or SIL3 is based on the analysis of the importance of the control loop in the whole production device, its impact on safety and other aspects.
But in China, these are simplified by people from all walks of life. Field instruments and actuators use ordinary ones that do not have SIL. Only the control system requires SIL, and it is not necessary to calculate whether a certain SIL is required. In petrochemical industry, SIS has become SIL 3.
[Recommended reading] / TECHNICAL ARTICLES


























